International
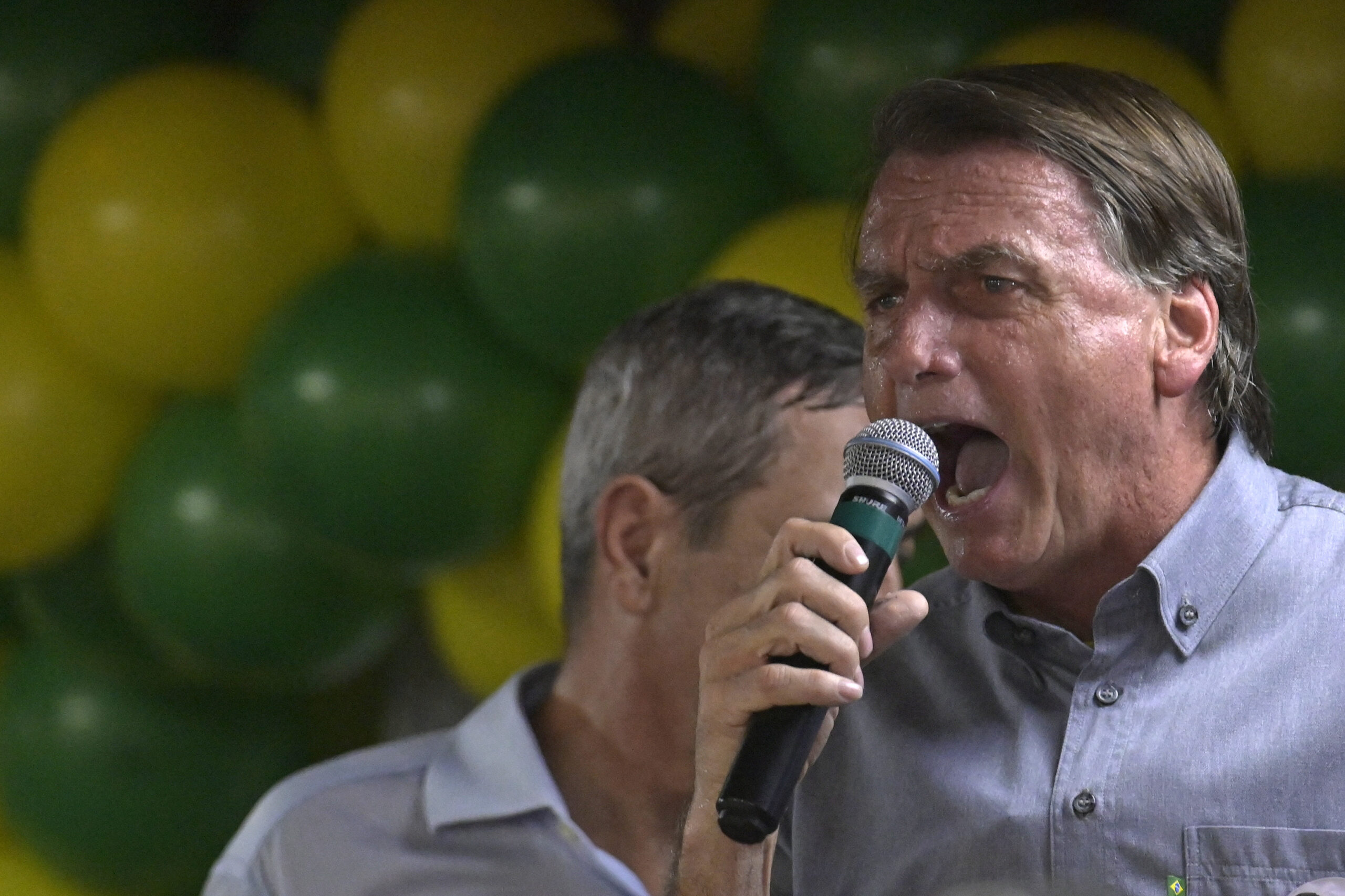
In Brazil, Bolsonaro’s far-right echoes Trump’s

| By AFP | Pascale Trouillaud |
“Bolsonarismo,” the Brazilian far-right movement built around President Jair Bolsonaro, shares much in common with ultra-conservatives in power in Europe — Hungary, Poland and soon Italy — but is closer to Donald Trump and the US alt-right.
Whether or not Bolsonaro wins his uphill fight for re-election against veteran leftist Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva in Brazil’s October 30 runoff, the far-right’s arrival in power in Brazil, as elsewhere, is linked to deep social upheaval, analysts say.
“All these far-right movements are rooted in an economic and social crisis that is growing worse by the year: rising inequality, declining income for the working and middle classes,” says Christophe Ventura, a Latin America specialist at the French Institute for International and Strategic Affairs (IRIS).
“That has triggered the rise of widespread mistrust.”
The response, he says, has followed a similar pattern internationally: a rejection of “rotten and incompetent” traditional politicians in favor of “virtuous citizens and a more authoritarian government” to right the wrongs unleashed by globalization and free trade — blamed for all ills.
In Europe, Italy’s Fratelli d’Italia, Hungary’s Fidesz, Poland’s Law and Justice party, the Sweden Democrats and France’s Rassemblement National and Reconquete all “accuse immigrants of causing every crisis and want to close the borders,” says Geraldo Monteiro, head of the Brazilian Center for Democracy Studies and Research at Rio de Janeiro State University (UERJ).
The Brazilian context is different: no longer a major immigration destination, “immigrants aren’t a big subject,” and Islamophobia and anti-Semitism are less prevalent than in Europe, says Monteiro.
Bolsonarismo’s version of “national solidarity” is instead a battle of “good people” versus the “corrupt.”
Internal enemies include the LGBT community, Indigenous peoples, environmental and human-rights activists, the media, academics and the cultural elite — all lumped together with Lula and the “communist” left.
Strong men
As with far-right movements everywhere, Bolsonarismo’s Holy Trinity is God, country and family.
The latter, say true believers, is under threat from gay marriage, abortion and “gender ideology.”
Whereas conservative Catholics are the core of the European far-right, in Brazil, it is the powerful, fast-growing Evangelical movement.
Bolsonaro’s movement is also more military in nature than its European cousins, says Monteiro.
He says Brazil “still carries the memory of the military dictatorship” (1964-1985) — fondly, in ex-army captain Bolsonaro’s case — and the president has actively courted military support, naming generals to powerful posts in his administration.
He has also energetically promoted gun ownership, signing a raft of legislation and decrees intended to help “good people” defend themselves and their property — a viewpoint that “doesn’t exist in Europe,” says Ventura.
“The primary reference point” for Bolsonaro’s far-right has been Donald Trump’s United States, he adds, drawing parallels with the American alt-right and Tea Party movements.
It is a brand of populism in which “the leader is the direct representative of the people,” says Mayra Goulart, a political scientist at Rio de Janeiro Federal University (UFRJ).
Anything supporters perceive as interfering with that direct democracy — political parties, institutions, the media — comes under attack.
Like the US alt-right, Bolsonaro’s movement has attacked Brazil’s democratic institutions as enemies of the people, notably the Supreme Court and the supposedly fraud-plagued election system.
Many observers fear a Brazilian version of Trump supporters’ attack on the US Capitol if Bolsonaro loses on October 30.
Like Trump — who recently gave him a glowing endorsement — Bolsonaro regularly insults journalists and attacks the “fake news” media.
He prefers to communicate directly with supporters on social media — which is inundated with “alternative truth” and conspiracy theories.
Hate speech
Trump’s influence is also visible in Bolsonaro’s climate-change skepticism and resistance to expert advice on handling Covid-19.
The US and Brazilian movements also share a “pro-market, pro-business discourse,” says Goulart.
Free speech is upheld as an absolute right — unfiltered hate speech and disinformation included.
Both Trump and Bolsonaro ran as political outsiders and achieved “unexpected” victories, says Monteiro.
And both “easily draw thousands of supporters into the streets.”
International
Arsenal stun Real Madrid at the Bernabéu to reach Champions League semifinals
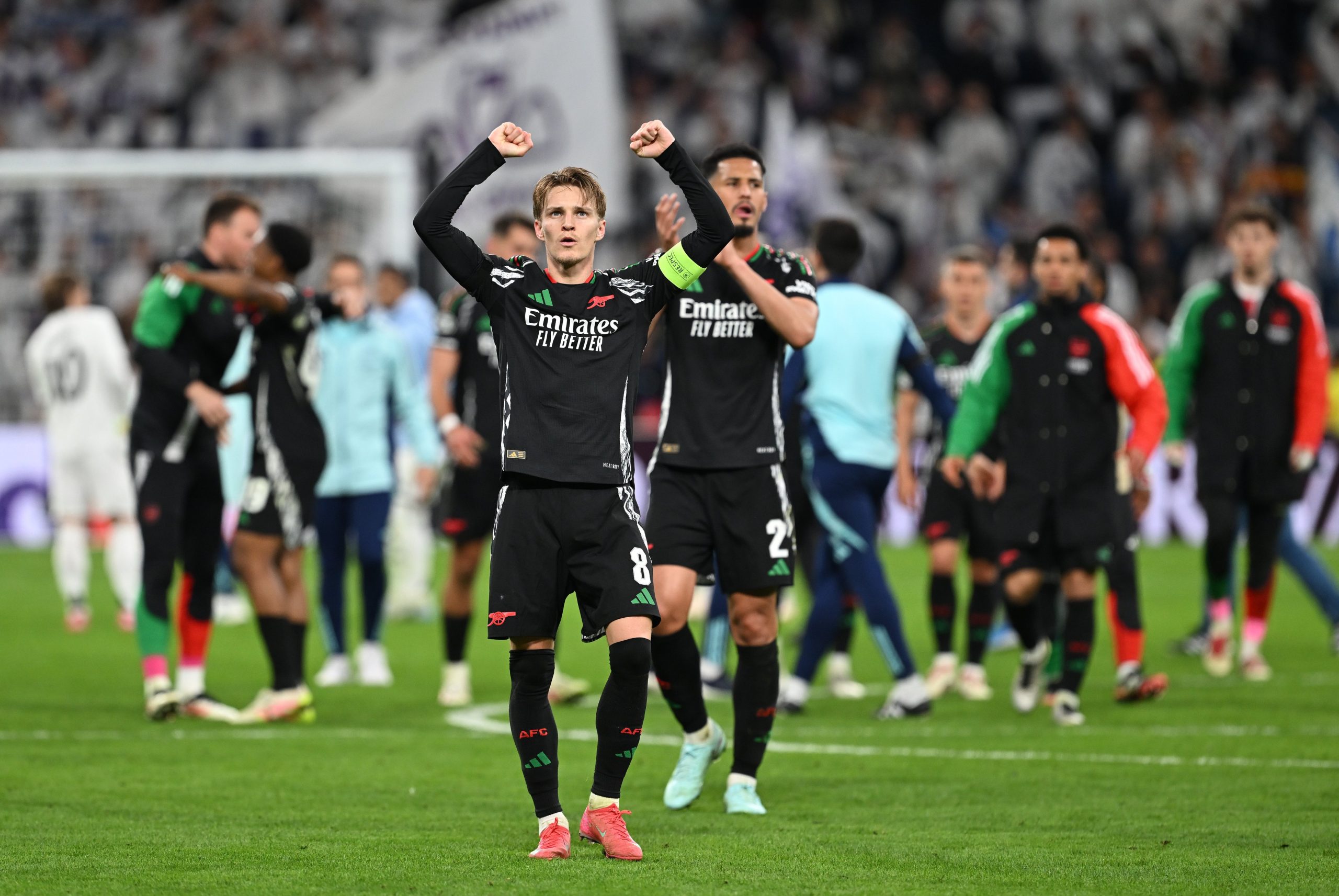

Arsenal enjoyed a “historic night” on Wednesday after defeating Real Madrid 2-1 at the Santiago Bernabéu, knocking them out of the Champions League quarterfinals, midfielder Declan Rice said.
“It’s such a special night for this club, a historic night for this club,” said Rice, who scored twice in the first leg in London, speaking to TNT Sports.
The English international was named Man of the Match in both legs — the 3-0 win in London and the second leg in Madrid.
“It’s amazing. I knew we were on an upward trajectory and we’ve done incredibly well in this competition. We deserve it and we have full confidence in our coach. Reaching the semifinals is unbelievable,” Rice added.
International
DeSantis’ immigration crackdown sparks alarm in Venezuelan Communities in Doral
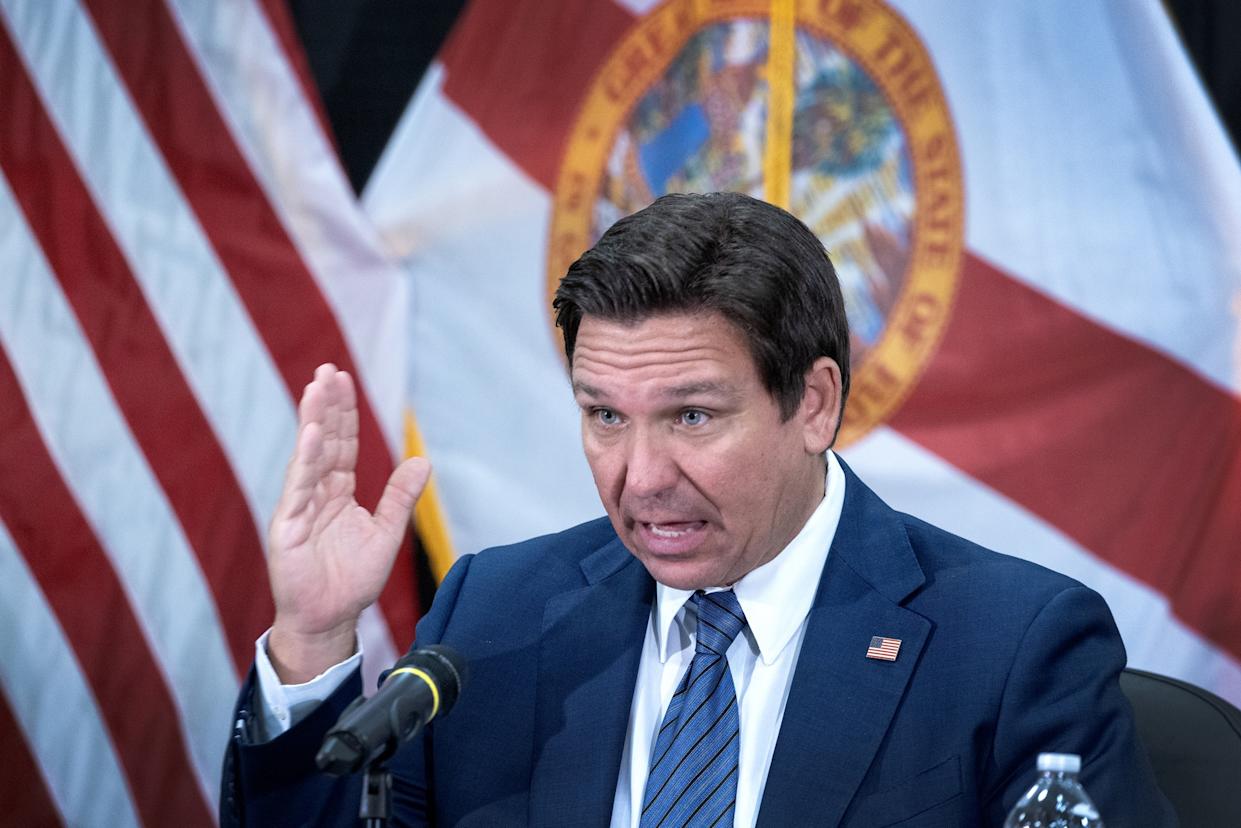

Florida, the U.S. state with the third-largest immigrant population, has become the most aggressive in targeting undocumented immigrants, largely due to pressure from Governor Ron DeSantis. This shift has led Latino-majority cities like Orlando and Doral to authorize their police forces to assist in immigration enforcement.
In Doral — part of the greater Miami area where 70.7% of residents are immigrants and 48% are of Venezuelan origin — the City Council is expected to approve a measure this Wednesday allowing local police to collaborate with Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), despite opposition from neighborhood groups and human rights activists.
“It’s yet another betrayal,” said Susana Ríos, a 57-year-old Venezuelan woman currently under Temporary Protected Status (TPS), whose extension was denied by the White House and is now being challenged in court.
Meanwhile, José González, a 21-year-old immigrant, said he feels “abandoned.” He can’t stop thinking about the images of Venezuelans deported to El Salvador without due process. “We’re all in danger,” he warned.
International
Bogotá residents line up for yellow fever vaccine amid national alert
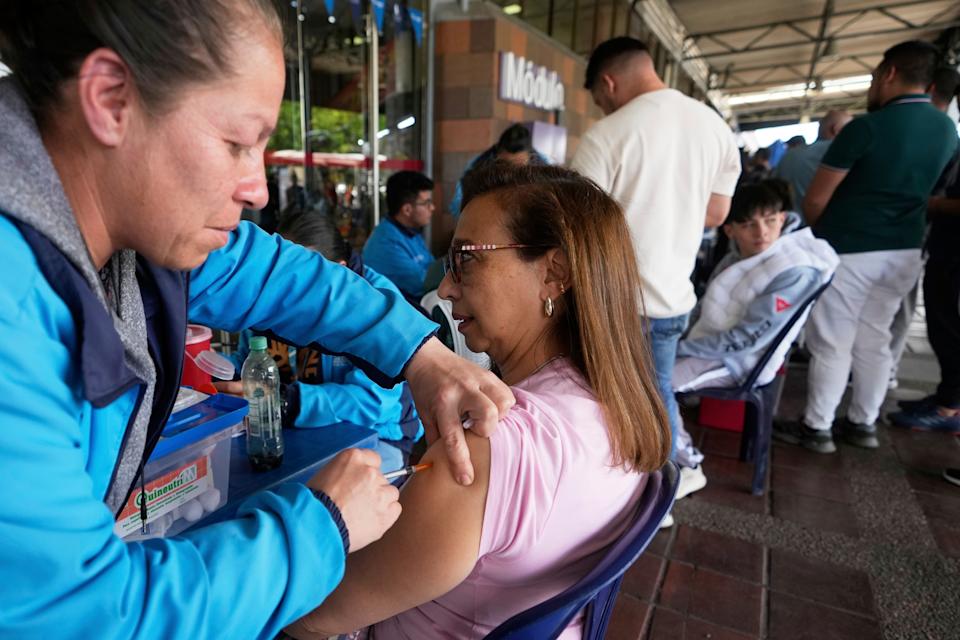
David Suárez went to a public health center in Bogotá on Wednesday to get vaccinated against yellow fever. It wasn’t originally in his plans, but he responded to a call made just hours earlier by President Gustavo Petro, who announced he will declare a health and economic emergency due to a new outbreak of the disease that has already left more than 30 people dead, mostly in the central-western region of the country.
“I got vaccinated for two reasons: first, for my own health because I’m traveling, and second, for a social reason — simply to follow the president’s guidance and be aware that this is a problem for all of us,” said Suárez, a 39-year-old teacher, to The Associated Press.
Like Suárez, dozens of people were waiting in line for the vaccine at Bogotá’s main intercity bus terminal, a key transportation hub especially crowded during travel seasons like Holy Week.
The teacher is traveling with his family to the department of Huila, which has activated a contingency plan due to its proximity to Tolima — the epicenter of the yellow fever outbreak — where a state of public calamity has been declared.
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoNightclub Collapse in Dominican Republic Claims 226 Lives
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoSpanish Ex-Congresswoman Calls for ‘Bukele-Style’ Security Policies in Europe
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoVenezuela accuses Guyana of “warlike intentions” after UK defense deal
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoTrump Authorizes Military to Take Control of Federal Land Along U.S.-Mexico Border
-

 Central America2 days ago
Central America2 days agoHonduran Police Offer $135K for Tips Leading to the Arrest of Romeo Vásquez
-

 Central America1 day ago
Central America1 day agoPetro questions Ecuador’s vote, cites reports of military control and arrests
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMPV Denounces Electoral Blockade as Secretary-General is Disqualified for May Elections
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMaduro Plans Major Workers’ March on May 1st to Defend Venezuela’s Freedom
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoColombia: Search continues for missing limb of italian scientist found dismembered
-

 International42 mins ago
International42 mins agoArsenal stun Real Madrid at the Bernabéu to reach Champions League semifinals
-

 International1 hour ago
International1 hour agoBogotá residents line up for yellow fever vaccine amid national alert
-

 International1 hour ago
International1 hour agoMexico refuses to restore ties with Ecuador while Noboa remains in office
-

 International49 mins ago
International49 mins agoDeSantis’ immigration crackdown sparks alarm in Venezuelan Communities in Doral















