Central America
Threats from the migratory route in Guatemala: dengue, arrests and climate change
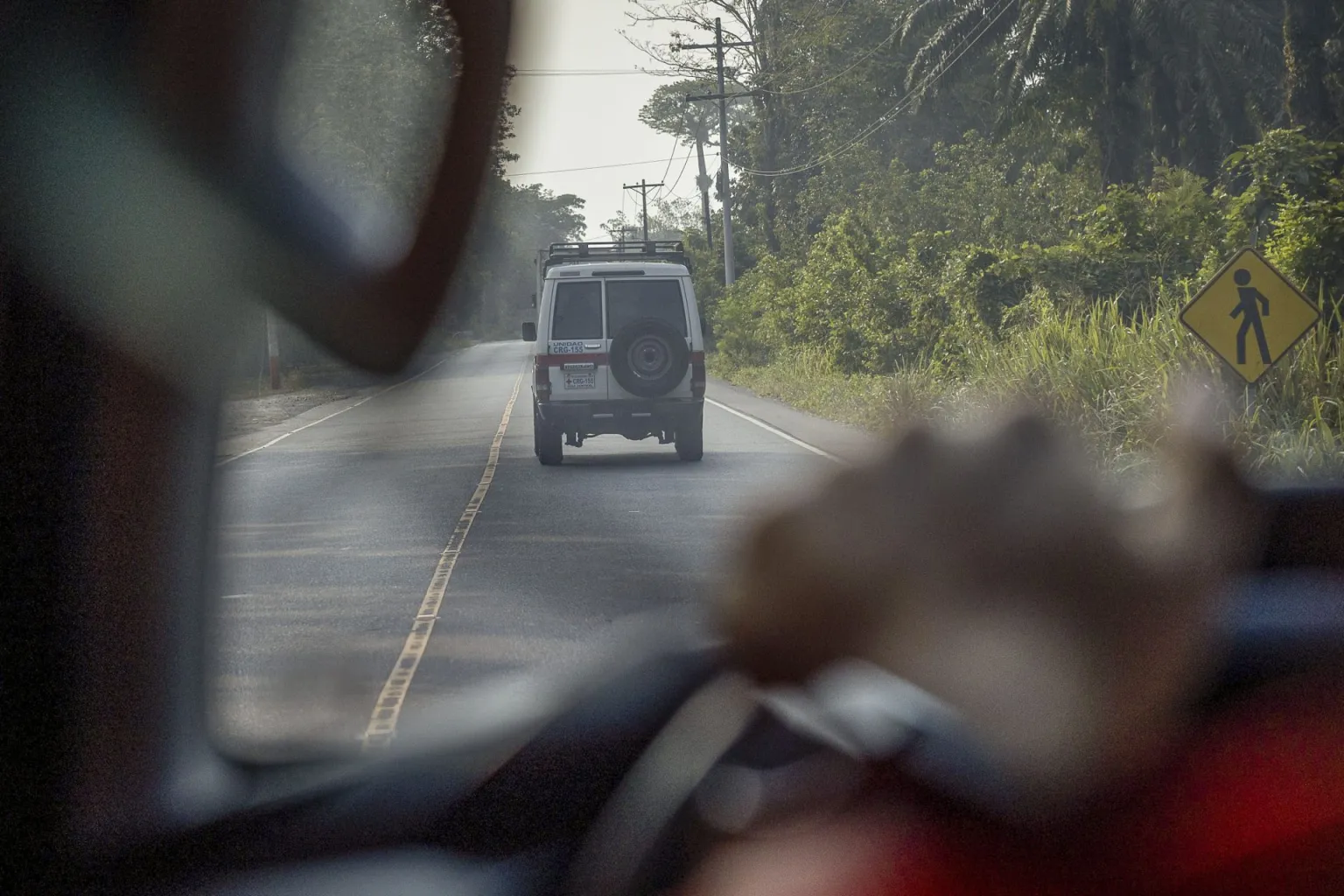

Thousands of migrants cross the border between Honduras and Guatemala daily on their way to the United States, facing the threat of tropical diseases such as dengue, the arrest of security forces and their subsequent deportation or the impact of a route hit by climate change.
On the border of El Corinto, between Guatemala and Honduras, the country’s Red Cross serves migrants who need medical assistance.
“Our job is to alleviate the suffering a little and dignify the lives of people who are in transit,” explains to EFE Mariana Bonilla, who works with the Red Cross at the Care Center for Migrants and Refugees (CAPMIR), located on the Guatemalan side of the border.
Every morning, Bonilla, 31, and the rest of her team, track the border road surrounded by African palm, banana plantations and the imposing Motagua River, the largest in Guatemala, in search of groups of migrants to guide them and indicate the points where they can receive support.
Within its center of attention, supported by the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC), migrants receive both medical and psychosocial assistance. “Many come with traumas from their passage through the Darién jungle” between Colombia and Panama, explains Bonilla.
Two kilometers after crossing the border, on the migratory route, is the village of Jimeritos, a community made up of farmers dedicated mainly to the cultivation of bananas that for six years has turned its small communal room into a refuge for migrants to rest.
“We are motivated to work with migrants. They leave their countries to seek an improvement for their family and here we give them what we can, because we do not know when we will have the same need,” explains Felicita Palencia, a resident of Jimeritos who was trained by the Red Cross to take care of migrants.
The community lounge has a bedroom with capacity for 12 people and, according to the leaders of the village, there are nights where they receive up to 30 migrants who seek refuge before continuing their journey to the Mexican border of Tecún Umán, located about 540 kilometers at the other end of the country.
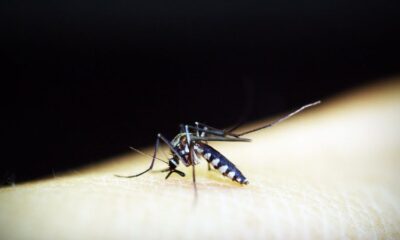
Community community members pay attention despite the difficulties they are going through, such as strong dengue epidemics that affect the department of Izabal, where in 2023 more than 500 cases were registered and the region was put on red alert by the health authorities, a disease from which migrants are not freed either.
On May 2, in the community room, the Red Cross gathered the children of the Jimeritos public primary school to give them a talk about hygiene and sanitation measures to eliminate the mosquito that transmits dengue, as well as tools to identify the symptoms of this disease.
Carlos Linares, who has lived in this migrant host village for 42 years, assures EFE that the biggest concern for them is climate change, since the rainy season is approaching and in years such as 2001 and 2020 many houses were destroyed by storms.
“This part of the road is the most difficult to get to the United States, because there are a lot of police and they can return us to Honduras,” Mario Alvarado, a Honduran migrant who decided to look for the “American dream,” explains to EFE.
With temperatures of 40 degrees, Alvarado crossed the border, bordering the Motagua River and the African palm plantations, to end up arrested by the Guatemalan authorities.
Alvarado is the third time he has been on his way to the United States. He does it with his compatriot Danny Gámez, the same one with whom a few months ago they were deported from Texas, United States, after a journey that allowed them to work in the North American nation as painters.
Like Alvarado and Gámez, thousands of migrants seek to cross Guatemala every year and so far in 2024 alone, almost 8,000 have been arrested by the security forces for their subsequent deportation, according to figures from the Guatemalan Migration Institute (IGM).
“It doesn’t matter how many times we are deported. If there are no conditions to live in Honduras, we will always find a way to leave again,” Alvarado reiterates, before moving away between the path of a plantation with his journey companion.
Central America
Nicaragua Held Responsible for Harassment of Opposition Prosecutor and His Family

The Inter-American Court of Human Rights on Wednesday found Nicaragua responsible for threats, harassment, and attacks suffered by opposition election monitor Jaime Antonio Chavarría and his family after he reported irregularities during the July 27, 2008 municipal elections.
Chavarría was serving as an electoral verification prosecutor for the opposition Constitutional Liberal Party at a polling station in Managua on election day. He filed a formal objection with local authorities, complaining that the polling center had closed before the scheduled time while voters were still waiting to be verified.
According to the ruling, Chavarría and several relatives present at the site were subjected to insults and threats by a representative of the ruling Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN). As they were leaving the area, they were intercepted and attacked by a large group of individuals allegedly incited by local Sandinista leaders.
“The events were witnessed by police officers who refrained from intervening. Mr. Chavarría Morales and his relatives, who suffered various injuries, managed to escape in their vehicle, which the aggressors attempted to set on fire,” the court detailed.
Chavarría reported the incident to the National Police, but the case was ultimately shelved in May 2016. Acts of harassment and intimidation continued over time.
The court concluded that the State bore responsibility for the threats, harassment, and subsequent attacks following July 2008, citing the participation or acquiescence of state agents in some of the incidents, as well as the failure to adopt protection and investigative measures.
In its judgment, the court determined that Nicaragua violated Chavarría’s rights to personal integrity, freedom of thought and expression, political rights, equality before the law, and the right to defend human rights.
The ruling also established state responsibility for violations affecting the personal integrity, judicial guarantees, judicial protection, and family protection rights of Chavarría and for the harm caused to the life plans of his children: Cindy Alicia Chavarría Alonso, Jeffer Joaquín Chavarría Alonso, and Jaime Antonio Chavarría Alonso.
Central America
Guatemala’s Attorney General Fails in Bid for Top Court Seat Amid Corruption Allegations

The Attorney General of Guatemala, Consuelo Porras, failed on Tuesday in her bid to join the country’s highest constitutional court, a position that would have granted her immunity from corruption allegations for which she has been sanctioned by the United States and the European Union.
Porras, whose term as attorney general ends in May, did not receive a single vote in the final round of voting to become a magistrate of the Corte de Constitucionalidad, whose rulings are final and cannot be appealed.
The Supreme Court reelected Dina Ochoa and Claudia Paniagua as its representatives to the Constitutional Court.
Ochoa is considered close to former presidents Jimmy Morales (2016–2020) and Alejandro Giammattei (2020–2024), both accused of corruption. Paniagua, like Porras, has been sanctioned by the United States.
Washington and the European Union have labeled Porras as “corrupt” and “undemocratic,” accusing her of attempting to block the inauguration of Social Democratic President Bernardo Arévalo two years ago.
In addition, the 72-year-old attorney general—who is seeking a third term—has been accused of forcing anti-corruption officials, journalists, and social leaders into exile. She denies the allegations and claims they are part of a political persecution campaign.
Porras’ chances of remaining in office, a position she has held since 2018, are considered slim, as President Arévalo is responsible for appointing the next attorney general.
Central America
Panama Canal Monitoring Trade as Middle East Conflict Disrupts Shipping
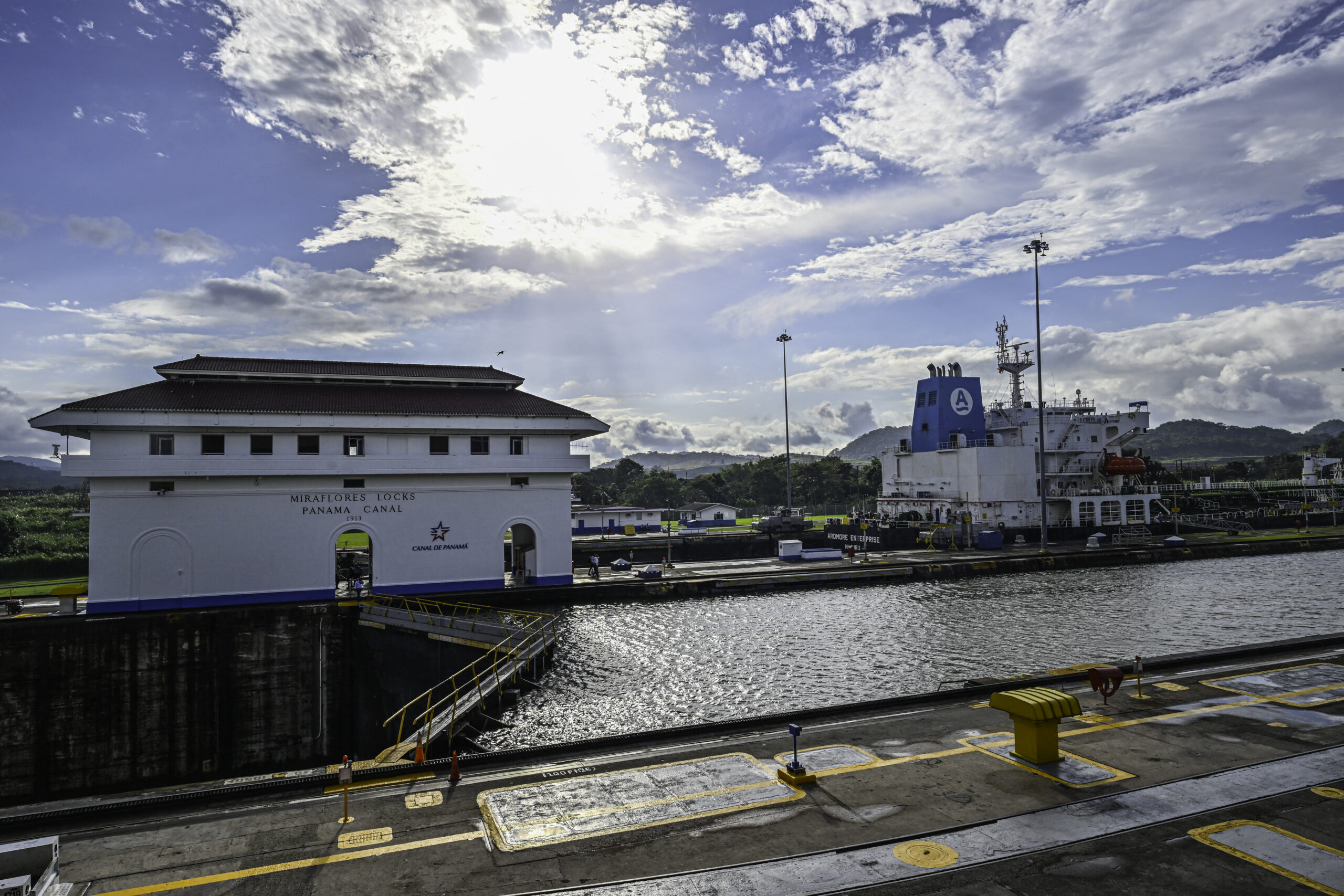

The Panama Canal Authority (ACP) said Monday it is closely monitoring global maritime trade developments following the conflict triggered by joint U.S. and Israeli strikes against Iran.
However, the ACP described it as “premature” to predict potential consequences for vessel traffic through the interoceanic waterway, which handles roughly 5% of global maritime trade.
“The Panama Canal continuously monitors the evolution of international maritime trade and the dynamics that may influence its flows,” the authority said in a statement. The canal’s main users are the United States and China, connecting primarily the U.S. East Coast with Asia, including South Korea and Japan.
The ACP emphasized that the canal “continues to operate safely, efficiently, and reliably,” providing uninterrupted service to the global maritime community.
Global Shipping Disruptions
The U.S.-Israeli military operation against Iran and Tehran’s retaliatory actions have disrupted global maritime traffic, particularly oil tanker routes.
Shipping giants Maersk and CMA CGM have suspended transits through the Strait of Hormuz as well as crossings via the Suez Canal, the key route linking the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea.
As a result, cargo vessels are now rerouting around Africa to reach Europe from the Middle East and Asia — a detour that adds several thousand kilometers and several days to voyages.
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoWhite House Says Spain Agrees to Cooperate with U.S. Military After Trump Threatens Trade Embargo
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoSpain’s Prime Minister to Address Nation Amid Trump’s Trade Threats
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoClaudia Sheinbaum: Operation Against ‘El Mencho’ Was Based on Pending Arrest Warrants
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoNew York Announces First 2,000 Seats in Universal 2-K Program
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoSpain Denies Any Agreement to Cooperate with U.S. Military in Iran Operations
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoNicaragua Held Responsible for Harassment of Opposition Prosecutor and His Family
-

 Central America5 days ago
Central America5 days agoGuatemala’s Attorney General Fails in Bid for Top Court Seat Amid Corruption Allegations
-

 International5 days ago
International5 days agoWarner Bros. Developing First ‘Game of Thrones’ Movie With ‘Andor’ Writer
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoYoung Woman Will Represent Mexico at 2026 World Cup Opener, Says President Sheinbaum
-

 International17 hours ago
International17 hours agoTrump announces 17-nation alliance in the Americas to “destroy” drug cartels
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump replaces Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem with Senator Markwayne Mullin