Central America
Honduran president grants amnesty to husband’s allies

AFP
Honduras’ new president, leftist Xiomara Castro, who came to power promising to fight corruption, granted amnesty Saturday to many officials who served in her husband’s government more than a decade ago.
Manuel Zelaya was president from 2006-2009 until he was ousted.
The measure was approved on Thursday by the legislature led by Luis Redondo, a Castro loyalist, amid an ongoing dispute with a rival congressional faction over who should lead the body.
Despite that, Castro has pushed ahead with the amnesty and the measure was published Saturday in the Official Gazette, which gave it force of law.
The move drew criticism even from her new special advisor on transparency.
The unconditional amnesty is for officials who served in her husband’s government and those who were imprisoned for demonstrating against the re-election of President Juan Orlando Hernandez in 2017. He was Castro’s predecessor.
Zelaya was overthrown in 2009 by a civic-military alliance, which questioned his closeness to Venezuela’s socialist government.
Anti-corruption activists have claimed Castro’s pardons could cover the past deeds of people who engaged in corruption.
Castro replaced the right-wing Hernandez, who left power dogged by allegations of drug trafficking and corruption in a country where at least 60 percent of the 10 million inhabitants live in poverty.
Elected in November, the country’s first woman president faces an uphill struggle to reform a country with one of the highest murder rates in the world. Tens of thousands of its citizens have tried to flee to the United States.
International
Two fans killed in gate collapse outside Chile’s Estadio Monumental
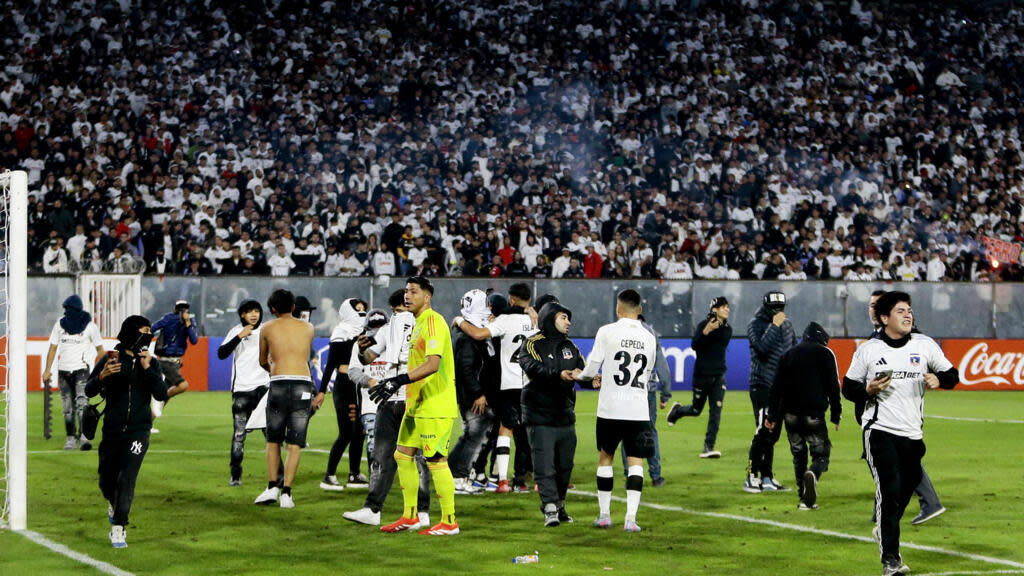

Two people lost their lives near the Estadio Monumental in Santiago, Chile, following a chaotic incident that occurred before the Copa Libertadores match between Colo Colo and Brazil’s Fortaleza on April 10. According to the Public Prosecutor’s Office, the victims were crushed after a fence on the stadium perimeter collapsed, though authorities are investigating whether a police armored vehicle may have played a role.
It was a black Thursday at Chile’s Estadio Monumental. Two local fans died outside the stadium after a yet-unclarified incident caused a metal gate to fall on them, leading to fatal asphyxiation.
Local media reports indicate that a group of fans attempted to force their way into the stadium before kickoff. In response, local police allegedly deployed armored vehicles to block the breach.
Preliminary reports cited by local newspapers and news agencies like EFE identify the victims as two young individuals—one 18 years old and the other just 13.
Central America
Nicaragua seeks ICJ intervention in Gaza conflict amid escalating violations

The Government of Nicaragua announced on Thursday that it has once again requested the International Court of Justice (ICJ) of the United Nations to intervene “as part” of the legal proceedings initiated by South Africa against Israel, accusing it of violating the 1948 Genocide Convention with its ongoing war in the Gaza Strip since October 7, following an attack by the Islamist group Hamas on Israeli territory.
In a statement, the Nicaraguan government, led by Daniel Ortega and his wife Rosario Murillo, explained that on April 1, they had decided to discontinue the proceedings filed with the ICJ related to the “severe violations of the rights of the Palestinian people and state,” due to the “high financial cost” involved for a developing country like Nicaragua, which faces significant economic restrictions.
“However, in the last week, there has been an escalation in violations against the Palestinian people and even against international humanitarian services, clearly revealing Israel’s disregard for all international law norms and the total complicity, particularly of some Western countries, which have decided to continue their political, economic, and military support for those responsible for these crimes,” stated the Nicaraguan government.
In light of this, the government continued, and “making a great effort, Nicaragua has decided to notify the International Court of Justice that it wishes to continue with the legal proceedings regarding the violations of the rights of the Palestinian people.”
Central America
U.S. Government says deported migrants should remain in El Salvador for life
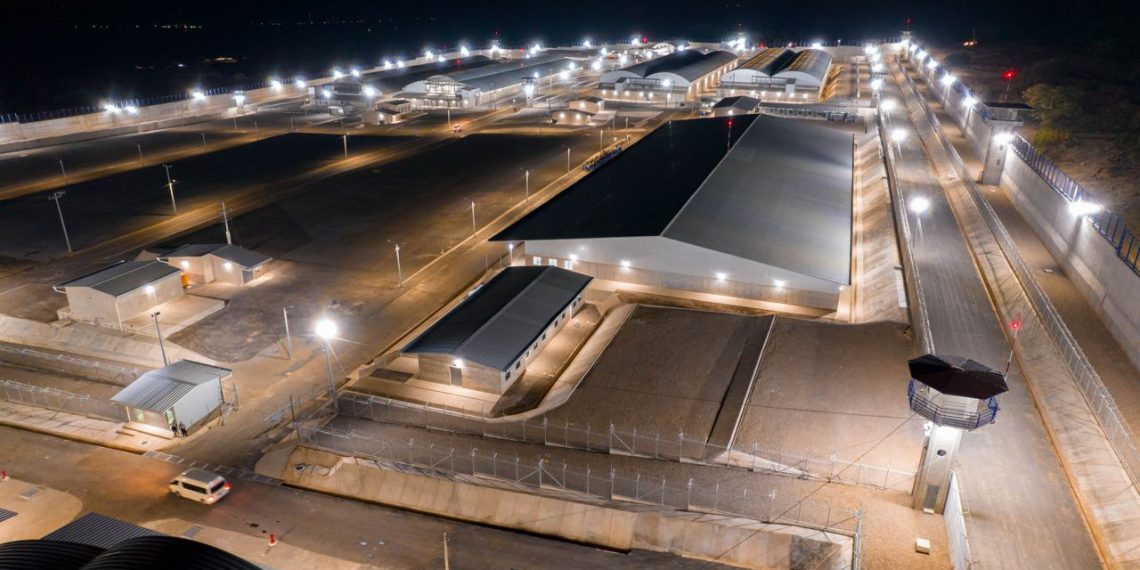

The United States government believes that the 238 migrants recently deported to El Salvador should remain in the country “for the rest of their lives.”
This was stated by Kristi Noem, the Secretary of Homeland Security, during a press conference. The following day, in a televised cabinet meeting, she reiterated the government’s commitment to continue its campaign to deport over 11 million people living in the U.S. without legal immigration status.
“We are confident that the people (sent to El Salvador) should be there, and they should stay there for the rest of their lives,” Noem told a group of reporters on Wednesday.
Despite the Trump administration’s defense of its decision to transfer the migrants to the Terrorism Confinement Center (Cecot), both testimonies from their families and reports from U.S. media outlets have shown that most of those currently detained there have no criminal backgrounds.
-

 International23 hours ago
International23 hours agoDominican Republic mourns over 200 dead in Jet Set nightclub collapse
-

 Central America5 days ago
Central America5 days agoHonduras Hosts CELAC Summit Amid Regional Concern Over U.S. Deportations
-

 Central America1 day ago
Central America1 day agoNicaragua seeks ICJ intervention in Gaza conflict amid escalating violations
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoRussia and US to Meet in Istanbul for Diplomatic Talks on April 10
-
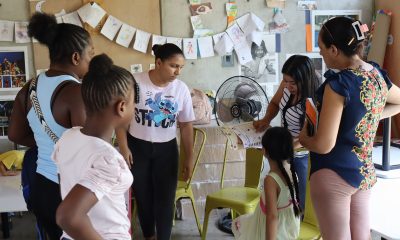
 International5 days ago
International5 days agoTeachers in Southern Mexico Bring Education to Stranded Migrant Children
-

 Central America2 days ago
Central America2 days agoMexico’s president proposes regional economic summit at CELAC
-

 Central America5 days ago
Central America5 days agoTrump Administration Asks Supreme Court to Block Return of Deported Salvadoran
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoAudit Exposes Major Breaches in Panama Canal Port Concession, $300 Million Owed to State
-

 Central America5 days ago
Central America5 days agoMulino and Orsi Highlight Shared Vision After Panama Joins Mercosur as Associate State
-

 Central America2 days ago
Central America2 days agoColombia to host fourth EU-CELAC Summit in November
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoMerengue concert turns to mourning as Jet Set collapse claims 136 lives
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoNeymar Returns to Santos Training After Month-Long Injury Layoff
-

 Central America2 days ago
Central America2 days agoCELAC condemns unilateral sanctions in ‘Tegucigalpa Declaration’
-

 Central America1 day ago
Central America1 day agoU.S. Government says deported migrants should remain in El Salvador for life
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoMaduro Announces Economic Emergency Decree Amid Growing Tensions with the U.S.
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoTransgender Student Arrested at Florida Capitol for Using Women’s Restroom Under New State Law
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoItalian biologist found dead in Colombia; investigation underway
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoScience Brings Back the Extinct Direwolf with Successful De-Extinction Project
-

 International23 hours ago
International23 hours agoVenezuelan oil shipments resume after tariff-induced delays
-

 International23 hours ago
International23 hours agoTwo fans killed in gate collapse outside Chile’s Estadio Monumental
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoMaduro signs Economic Emergency Decree to counter U.S. sanctions on Venezuela
-

 International23 hours ago
International23 hours agoConstitutional Court Removes Yoon: Lee Jae-myung’s Rise Sparks Warnings of a Radical Shift















