International
Cancer drug cooperation could save 1.5 mn lives a year: researchers
AFP
Around 1.5 million lives could be saved every year if the world worked together to more swiftly approve new cancer drugs, researchers said Tuesday.
The figure was based on how long it took two recent cancer drugs to be approved across the world after they were given the green light by the United States.
Pembrolizumab, an effective treatment for most lung cancers, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016.
More than 600,000 years of patients’ lives could have been saved if Brazil, Canada, China, India, Japan and the European Union had approved the drug at the same time, according to an analysis published in the Harvard Business Review, which is not peer-reviewed.
The authors, including US oncologist Bobby Daly, also looked at enzalutamide, which is used to treat prostate cancer.
Enzalutamide was approved by the FDA in 2012, but was not authorised in China for another seven years, partly due to a requirement for separate trials to be carried out there.
The analysis by members of the Bloomberg New Economy International Cancer Coalition found that 284,000 years of patient lives could have been saved if other countries had approved the drug alongside the FDA.
Extrapolating out from their findings, the researchers estimated that if each of the approximately seven cancer drugs approved by the FDA a year were authorised worldwide, it would reduce the number of cancer-related deaths by 10-20 percent.
That represents roughly 1.5 million of the around 10 million people who die of cancer every year.
‘Challenging’ for doctors
“In China alone an estimated 500,000 patient life-years could be saved through harmonisation of trial requirements that have delayed patient access to treatment,” former Australian prime minister Kevin Rudd, co-chair of the Bloomberg cancer coalition, said in a statement.
Mary Gospodarowicz, also a member of the coalition, said that it was “challenging” as an oncologist in Canada when a drug was approved in the US but would take years to be able to prescribe it to her patients.
The study assumed that the rest of the world had the infrastructure to diagnose and treat cancer as well as the US, which is not always the case, Gospodarowicz told AFP via phone from the World Cancer Congress in Geneva on Tuesday.
But it served as an example of how “removing the barriers to drug approval would be beneficial to patients around the world,” said the former president of the Union for International Cancer Control, which is holding the congress.
The authors of the analysis called on countries to embrace Project Orbis, a US-led framework aiming to get cancer drugs trialled and approved at the same time in multiple countries.
“The US has already made significant progress in setting up the regulatory infrastructure for cancer treatment with the Project Orbis initiative and the task ahead is to take that framework and internationalise it,” former New York mayor Michael Bloomberg said in a statement.
International
Peruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge

Peru is facing an unprecedented surge in crime ahead of its presidential election scheduled for April 12, with violence fueled by extortion networks and a wave of contract killings linked to organized crime.
Police data show that 2,200 homicides tied to organized crime were recorded in 2025, while extortion complaints increased by 19%, underscoring the growing security crisis in the South American nation.
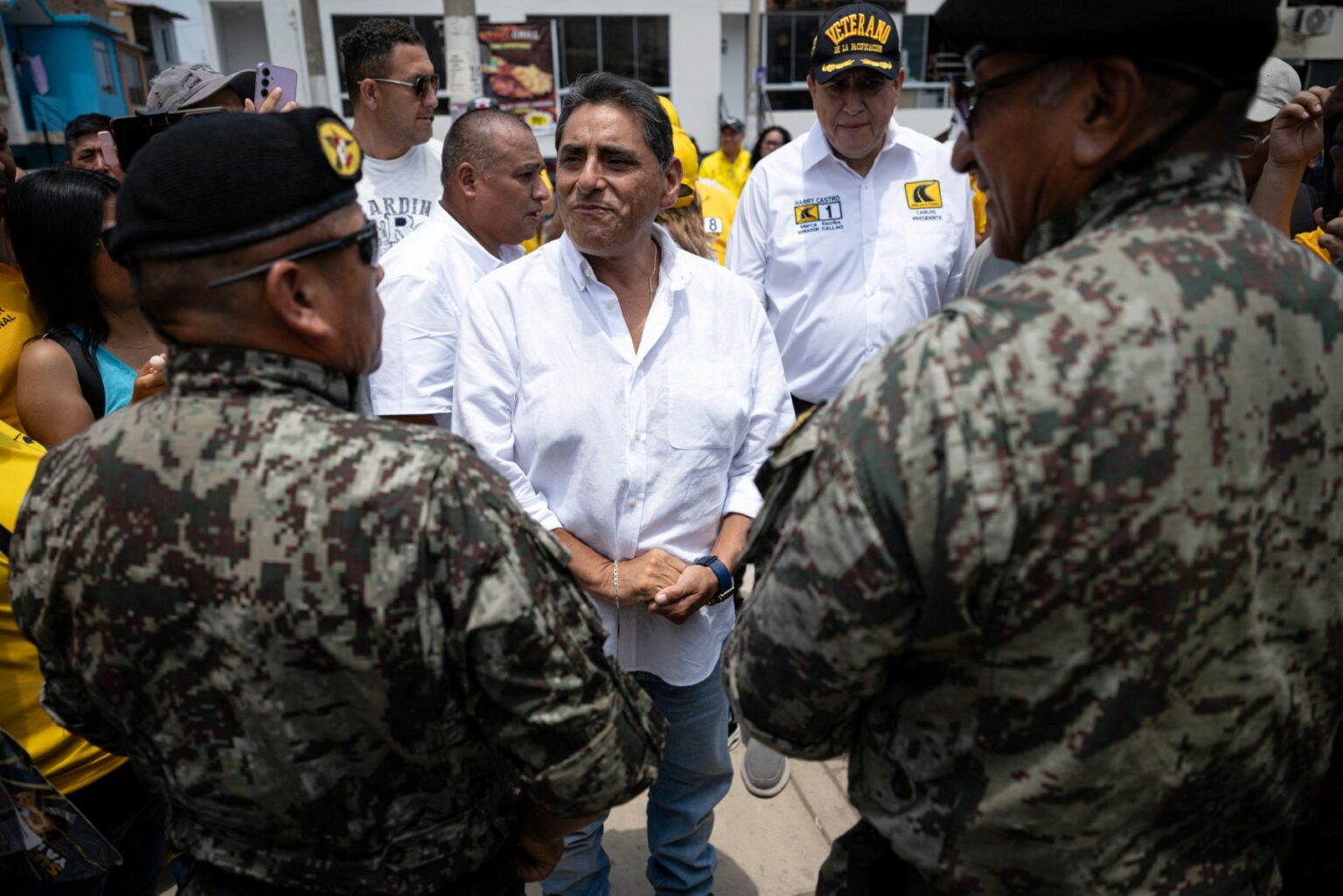
Amid this backdrop, presidential candidate Álvarez has proposed reinstating the death penalty if elected, arguing that extreme measures are needed to curb the violence.
To implement the proposal, Álvarez said Peru would withdraw from the American Convention on Human Rights—also known as the Pact of San José—which the country signed in 1978. The agreement prevents member states that have abolished capital punishment from reinstating it.
Currently, Peruvian law only allows the death penalty in cases of treason during wartime.
“We have to leave the Pact of San José and apply the death penalty in Peru because those miserable criminals don’t deserve to live,” Álvarez told AFP during a campaign stop at a market in Callao, the port city neighboring Lima.
“An iron fist against those criminals,” he added, proposing to declare hitmen as military targets.
During the campaign event, Álvarez walked through stalls selling vegetables, groceries, and fish, greeting vendors while musicians played cumbia music nearby.
The 62-year-old candidate, who spent more than four decades working in television as a comedian, is a newcomer to politics and is running for president under the País para Todos party.
Polls place him fifth in voter preference with nearly 4% support in a fragmented race featuring 36 candidates.
“I am an artist who has taken a step into politics to bring peace to my country,” Álvarez told reporters while surrounded by supporters.
International
FBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot

The man who died during Thursday’s attack on a synagogue in the United States suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head, according to the FBI.
FBI agent Jennifer Runyan told reporters that the suspect, identified as 41-year-old Lebanese citizen Ayman Mohamad Ghazali, shot himself at some point during the confrontation.
“At some point during the shooting, Ghazali suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head,” Runyan said during a press conference.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security confirmed the suspect’s identity.
Authorities said Ghazali drove a truck into the Temple Israel synagogue in West Bloomfield, located in the state of Michigan, on Thursday.
According to Michael Bouchard, sheriff of Oakland County, synagogue security personnel noticed the vehicle and confronted the suspect with gunfire.
Investigators said it would be premature to speculate about the motive for the attack, although reports indicate Ghazali recently lost relatives during Israeli strikes in Lebanon earlier this month.
“It would be irresponsible for me to speculate about his motive,” Runyan said.
Ghazali arrived in Detroit in 2011 on a spouse visa for U.S. citizens and obtained American citizenship in 2016, according to reporting by The New York Times.
He was the father of two teenagers, divorced from his wife in 2024, and had recently been working as a waiter.
The newspaper also reported that Ghazali attended a memorial service in the nearby city of Dearborn for relatives killed in the recent conflict, alongside other grieving family members from the Lebanese town of Machghara.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation said the incident is being investigated as an act of violence targeting the Jewish community.
A source from Michigan’s Lebanese-American community told CBS News that several of Ghazali’s relatives had been killed roughly ten days before the attack, leaving him deeply devastated.
International
Mexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba

Two logistics support vessels from the Mexican Navy — the ARM Papaloapan and the ARM Huasteco — docked again on Friday in the bay of Havana carrying a third shipment of humanitarian aid for Cuba.
The vessels had previously arrived on the Caribbean island on February 28 with a second cargo that included 1,200 tons of food, sent to help alleviate the country’s ongoing crisis, which has worsened following the U.S. oil restrictions affecting fuel supplies to the island.
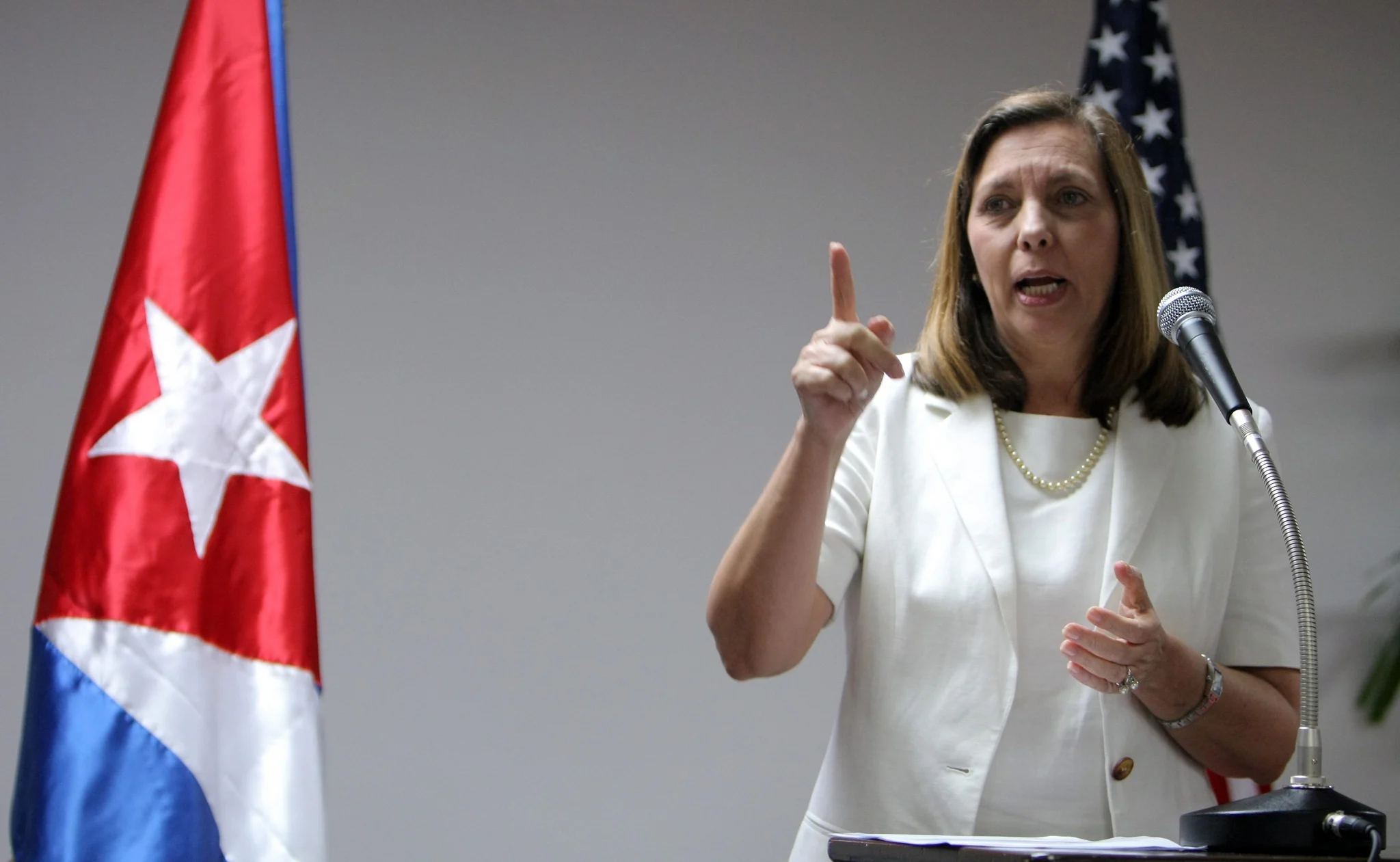
Cuba’s deputy foreign minister Josefina Vidal confirmed the new shipment in a social media post.
“Two ships carrying a third shipment of aid from the Government and the people of Mexico for the Cuban people are now arriving at the port of Havana. Thank you Mexico for your solidarity with Cuba,” she wrote.
Previous aid shipments
During the second shipment, the Papaloapan transported 1,078 tons of beans and powdered milk, while the Huastecocarried 92 tons of beans and 23 tons of assorted food products collected by social organizations with support from the government of Mexico City.
In recent months, Mexico has become the largest provider of humanitarian aid to Cuba, sending around 2,000 tons of supplies, mostly staple foods and hygiene products, in the two shipments prior to Friday’s delivery.
The first shipment alone included 814 tons of food.
Cuba praises Mexico’s support
Hours before the ships arrived, Cuban President Miguel Díaz-Canel highlighted Mexico’s support during a televised appearance, describing the country as “a friendly and brotherly nation that has shown tremendous solidarity,”particularly praising Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum.
Díaz-Canel also addressed reports suggesting that Mexican donations were being resold in state-run stores, dismissing them as a “disinformation campaign” promoted by right-wing groups.
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoU.S. Confirms Death of Six Crew Members in KC-135 Crash in Western Iraq
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoGuatemala Remains in “Restricted” Press Freedom Category, Chapultepec Index Warns
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump Says Iran Is Welcome at 2026 World Cup but Warns of Security Concerns
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoIran issues threat to Trump as conflict escalates over Strait of Hormuz
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Report Warns of Nicaragua’s “Transnational” Surveillance Network Targeting Dissidents
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoTrump Raises Possibility of “Friendly Takeover” of Cuba Amid Deepening Crisis
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoFBI Warns of Possible Iranian Drone Attack on U.S. West Coast
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoDriver detained after suspicious vehicle incident near the White House
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoEcuador Declares 60-Day National Emergency After Deadly Floods and Landslides
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoMexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba
-

 Sin categoría3 days ago
Sin categoría3 days agoUN experts warn Nicaragua runs vast transnational network to monitor exiled dissidents
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTrump Pushes for Regime Change in Cuba as Havana Confirms Talks With Washington
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Rapporteur Warns of “Deep Crisis” in Guatemala’s Judicial System
-

 International6 hours ago
International6 hours agoFBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot
-

 International6 hours ago
International6 hours agoPeruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge
-

 Sin categoría2 days ago
Sin categoría2 days agoFBI Most Wanted Fugitive Arrested in Mexico and Deported to U.S.




























