International
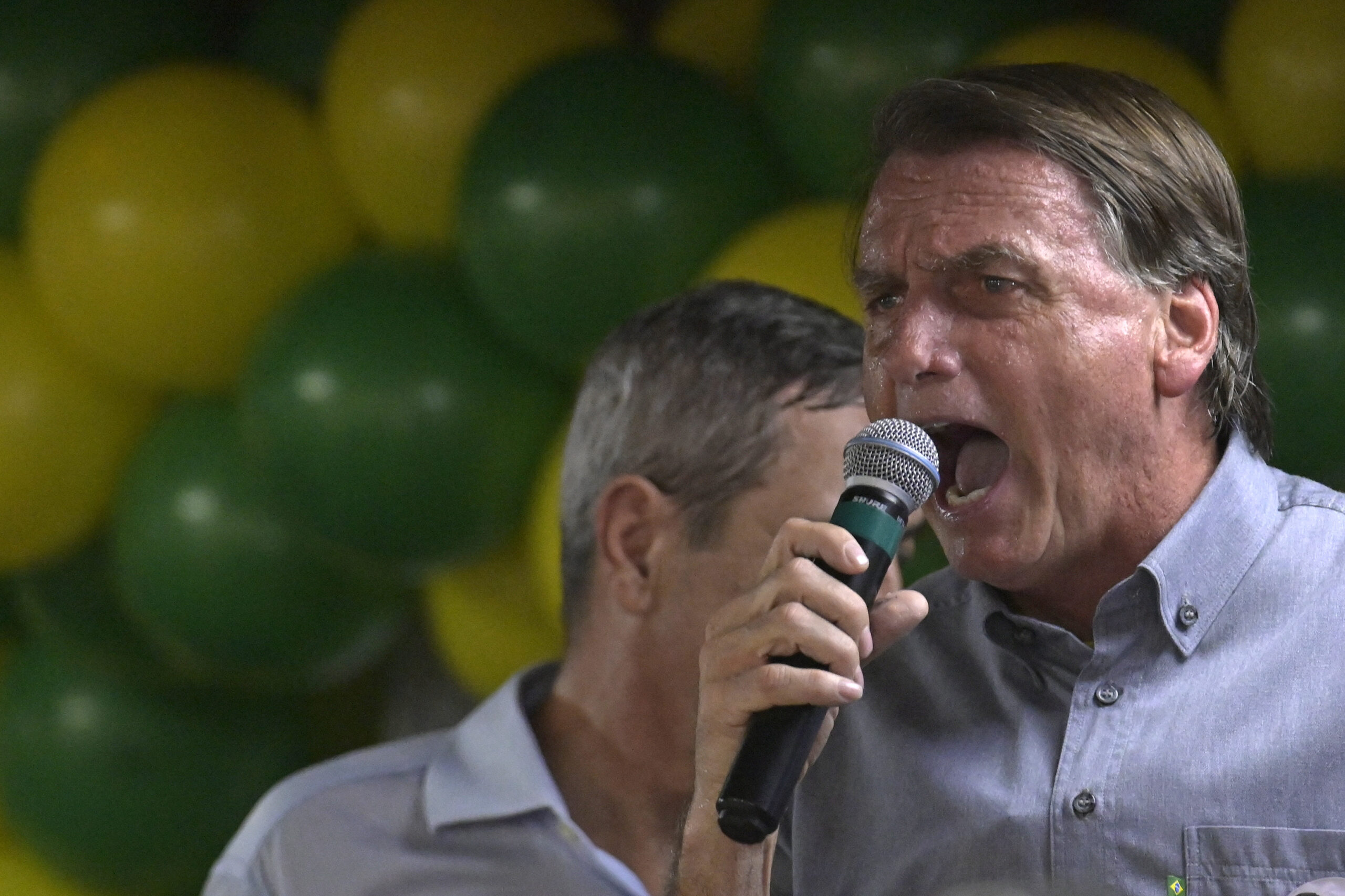
In Brazil, Bolsonaro’s far-right echoes Trump’s

| By AFP | Pascale Trouillaud |
“Bolsonarismo,” the Brazilian far-right movement built around President Jair Bolsonaro, shares much in common with ultra-conservatives in power in Europe — Hungary, Poland and soon Italy — but is closer to Donald Trump and the US alt-right.
Whether or not Bolsonaro wins his uphill fight for re-election against veteran leftist Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva in Brazil’s October 30 runoff, the far-right’s arrival in power in Brazil, as elsewhere, is linked to deep social upheaval, analysts say.
“All these far-right movements are rooted in an economic and social crisis that is growing worse by the year: rising inequality, declining income for the working and middle classes,” says Christophe Ventura, a Latin America specialist at the French Institute for International and Strategic Affairs (IRIS).
“That has triggered the rise of widespread mistrust.”
The response, he says, has followed a similar pattern internationally: a rejection of “rotten and incompetent” traditional politicians in favor of “virtuous citizens and a more authoritarian government” to right the wrongs unleashed by globalization and free trade — blamed for all ills.
In Europe, Italy’s Fratelli d’Italia, Hungary’s Fidesz, Poland’s Law and Justice party, the Sweden Democrats and France’s Rassemblement National and Reconquete all “accuse immigrants of causing every crisis and want to close the borders,” says Geraldo Monteiro, head of the Brazilian Center for Democracy Studies and Research at Rio de Janeiro State University (UERJ).
The Brazilian context is different: no longer a major immigration destination, “immigrants aren’t a big subject,” and Islamophobia and anti-Semitism are less prevalent than in Europe, says Monteiro.
Bolsonarismo’s version of “national solidarity” is instead a battle of “good people” versus the “corrupt.”
Internal enemies include the LGBT community, Indigenous peoples, environmental and human-rights activists, the media, academics and the cultural elite — all lumped together with Lula and the “communist” left.
Strong men
As with far-right movements everywhere, Bolsonarismo’s Holy Trinity is God, country and family.
The latter, say true believers, is under threat from gay marriage, abortion and “gender ideology.”
Whereas conservative Catholics are the core of the European far-right, in Brazil, it is the powerful, fast-growing Evangelical movement.
Bolsonaro’s movement is also more military in nature than its European cousins, says Monteiro.
He says Brazil “still carries the memory of the military dictatorship” (1964-1985) — fondly, in ex-army captain Bolsonaro’s case — and the president has actively courted military support, naming generals to powerful posts in his administration.
He has also energetically promoted gun ownership, signing a raft of legislation and decrees intended to help “good people” defend themselves and their property — a viewpoint that “doesn’t exist in Europe,” says Ventura.
“The primary reference point” for Bolsonaro’s far-right has been Donald Trump’s United States, he adds, drawing parallels with the American alt-right and Tea Party movements.
It is a brand of populism in which “the leader is the direct representative of the people,” says Mayra Goulart, a political scientist at Rio de Janeiro Federal University (UFRJ).
Anything supporters perceive as interfering with that direct democracy — political parties, institutions, the media — comes under attack.
Like the US alt-right, Bolsonaro’s movement has attacked Brazil’s democratic institutions as enemies of the people, notably the Supreme Court and the supposedly fraud-plagued election system.
Many observers fear a Brazilian version of Trump supporters’ attack on the US Capitol if Bolsonaro loses on October 30.
Like Trump — who recently gave him a glowing endorsement — Bolsonaro regularly insults journalists and attacks the “fake news” media.
He prefers to communicate directly with supporters on social media — which is inundated with “alternative truth” and conspiracy theories.
Hate speech
Trump’s influence is also visible in Bolsonaro’s climate-change skepticism and resistance to expert advice on handling Covid-19.
The US and Brazilian movements also share a “pro-market, pro-business discourse,” says Goulart.
Free speech is upheld as an absolute right — unfiltered hate speech and disinformation included.
Both Trump and Bolsonaro ran as political outsiders and achieved “unexpected” victories, says Monteiro.
And both “easily draw thousands of supporters into the streets.”
Central America
Trump Administration Asks Supreme Court to Block Return of Deported Salvadoran

The Trump administration on Monday asked the U.S. Supreme Court to block a lower court order requiring the return of a Salvadoran migrant who was mistakenly sent to a maximum-security prison in El Salvador, despite having legal protection from deportation.
The U.S. government has until Monday to bring Kilmer Armado Ábrego García back to the United States, as ordered by Judge Paula Xinis in a Maryland court.
According to The Washington Post, the administration argues it lacks authority to comply because Ábrego García is currently in Salvadoran custody.
The U.S. had appealed Judge Xinis’ ruling to the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals, but the court declined to act immediately—prompting the administration to take the case to the Supreme Court. In its filing, the government stated that “the Constitution entrusts the President, not federal district courts, with the conduct of foreign diplomacy and the protection of the nation from foreign terrorists, including through deportation.”
Ábrego García, a resident of Prince George’s County, Maryland, and married to a U.S. citizen, came under scrutiny in 2019 after an informant claimed he was a member of the MS-13 gang (Mara Salvatrucha).
Although he was initially slated for deportation, a judge later granted him a stay of removal after he requested asylum, according to the lawsuit.
Nevertheless, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) detained him on March 12, claiming his status had changed, and sent him to a detention center in Texas.
International
Teachers in Southern Mexico Bring Education to Stranded Migrant Children
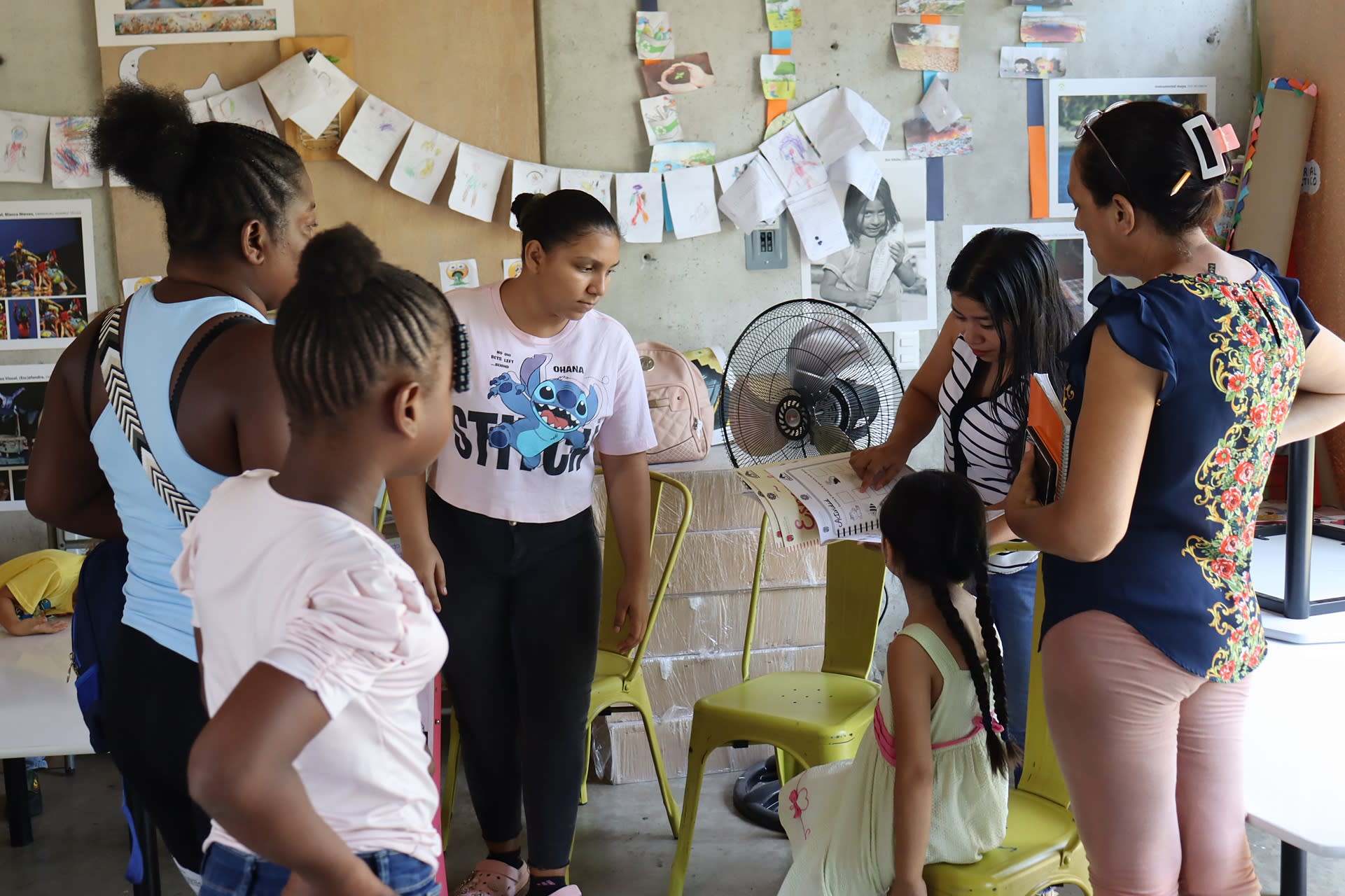
Teachers in southern Mexico have created a program to provide classes for migrant children stranded in the region, following a year-over-year increase of over 70% in irregular migration among minors—many of whom lose months or even years of education during their journey toward North America.
In Tapachula, the largest Mexican city bordering Central America, three teachers offer preschool, elementary, and secondary education through the Chiapas State Migrant Education Program (Pemch).
This initiative has been replicated in key municipalities across Chiapas, including San Cristóbal de Las Casas, the capital Tuxtla Gutiérrez, Palenque, Comitán, and other border towns. Currently, there are around 1,345 migrant students and a total of 35 teachers working across farms and shelters.
Pablo Arriaga Velázquez, a teacher with the migrant education program in Tapachula, told EFE that the project was born in response to the large number of migrant minors, as enrolling them in regular schools is often difficult.
Central America
Mulino and Orsi Highlight Shared Vision After Panama Joins Mercosur as Associate State

The Presidents of Panama, José Raúl Mulino, and Uruguay, Yamandú Orsi, highlighted on Monday the path of integration both countries have undertaken in areas such as trade and the defense of democracy, following a meeting held at the Panamanian government headquarters.
In a brief statement to the press, both leaders emphasized that Panama and Uruguay share many values and are working together across different sectors. They also underlined a renewed connection following Panama’s accession last December to the Southern Common Market (Mercosur) as an Associated State.
“Panama has begun a new era of looking southward, seeking opportunities not only for work, business, and friendship, but also for regional integration in a positive sense. Today, I believe we have taken a decisive step in that direction,” said President Mulino.
The Panamanian leader stressed that his country and Uruguay “have much in common” and share “important values in terms of democracy, respect for institutions, and the rule of law—principles that must always be strengthened, no matter how much effort it takes.”
-

 Internacionales2 days ago
Internacionales2 days agoErik Prince Backs Ecuador’s Daniel Noboa in Fight Against Crime and “Narcoterrorism”
-

 Central America3 days ago
Central America3 days agoPanama’s former president Martinelli claims political enemies tried to kill him
-

 Central America2 days ago
Central America2 days agoGuatemala’s Legal Chief Shot Dead in Parking Lot: Investigation Underway
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoJavier Milei vows to work ‘side by side’ with the U.S. on trade rules
-

 Central America13 hours ago
Central America13 hours agoHonduras Hosts CELAC Summit Amid Regional Concern Over U.S. Deportations
-
 International13 hours ago
International13 hours agoTeachers in Southern Mexico Bring Education to Stranded Migrant Children
-

 Central America13 hours ago
Central America13 hours agoMulino and Orsi Highlight Shared Vision After Panama Joins Mercosur as Associate State
-

 Central America13 hours ago
Central America13 hours agoTrump Administration Asks Supreme Court to Block Return of Deported Salvadoran















