International
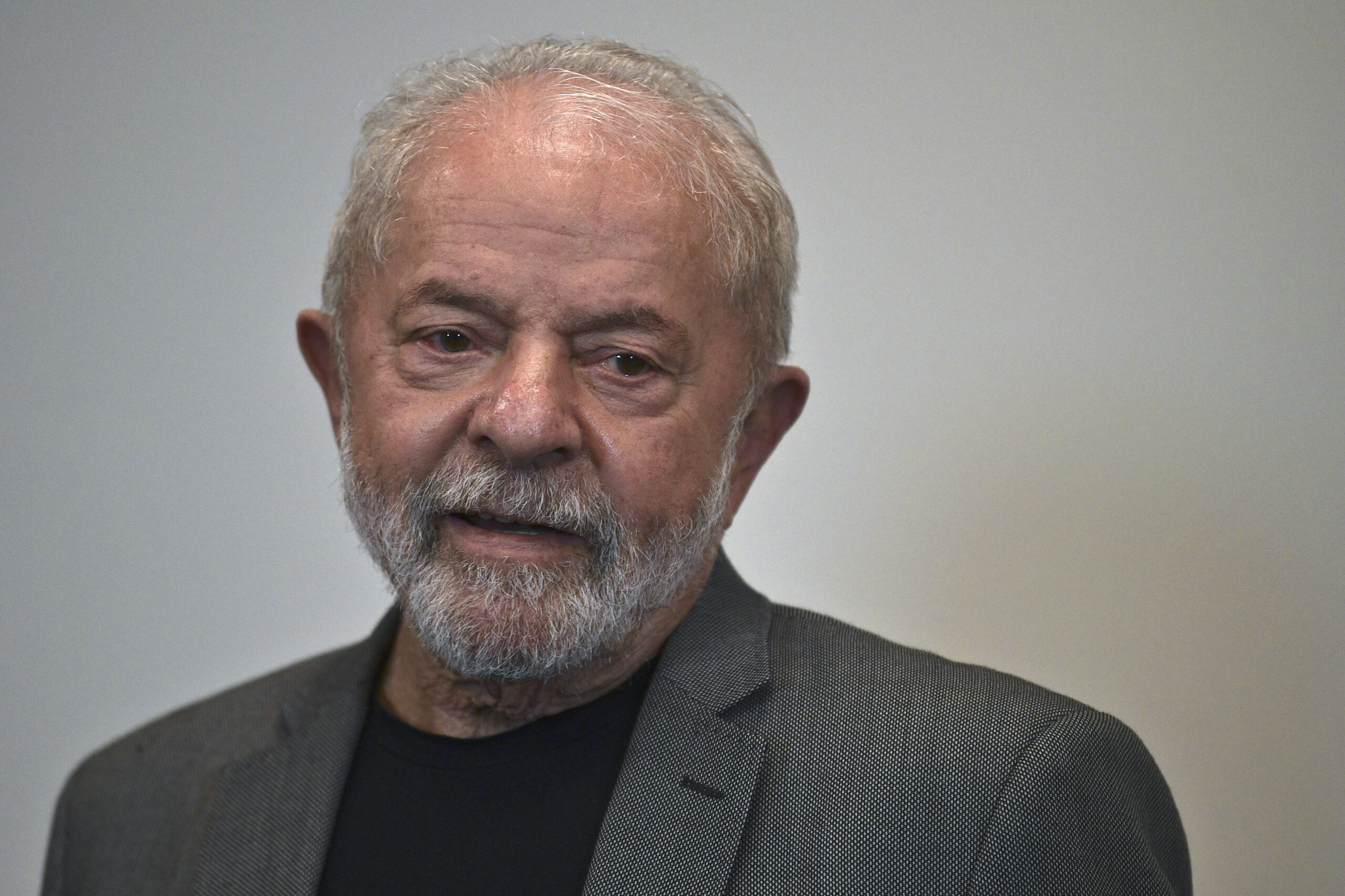
Tough choices as Brazil’s Lula gets down to business

| By AFP | Marcelo Silva De Sousa
Fresh off a celebratory beach holiday, Brazilian president-elect Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva got down to uglier business Monday: figuring out how to govern with a hostile Congress, nasty budget crunch and impossible-looking to-do list.
The political horse-trading of the transition period now starts in earnest for the veteran leftist, who will be sworn in for a third term on January 1, facing a far tougher outlook than the commodities-fueled boom he presided over in the 2000s.
Lula, 77, celebrated his narrow win over far-right incumbent Jair Bolsonaro in the October 30 runoff election by escaping last week to the sun-drenched coast of Bahia in northeastern Brazil.
He joked he needed a belated honeymoon with his first-lady-to-be, Rosangela “Janja” da Silva, whom the twice-widowed ex-metalworker married in May.
His other honeymoon — the political one — could be short, analysts say.
Lula is meeting Monday with advisers in Sao Paulo. On Tuesday, he will travel to the capital, Brasilia, to finish assembling his 50-member transition team and start negotiating with members of Congress, two allies told AFP.
He faces a battle to get bills passed in a legislature where conservatives scored big gains in October’s elections.
Lula’s coalition has around 123 votes in the 513-seat Chamber of Deputies, and 27 in the 81-seat Senate, meaning he will have to strike alliances to get anything done — and even just survive, given the threat of impeachment in Brazil, where two presidents have been impeached in the past 30 years.
Into the shark tank
Lula is expected to meet in Brasilia with lower-house speaker Arthur Lira, a key Bolsonaro ally from the loose coalition of parties known as the “Centrao,” a group known for striking alliances with whoever is in power — in exchange for feeding on the federal pork barrel.
Lula will be under pressure from the Centrao not to oppose the so-called “secret budget”: 19.4 billion reais ($3.8 billion) in basically unmonitored federal funding that Bolsonaro agreed to allocate to select lawmakers to boost support for his reelection bid.
Meanwhile, money will be tight for Lula’s campaign promises, including increasing the minimum wage and maintaining a beefed-up 600-reais-per-month welfare program, “Auxilio Brasil.”
Bolsonaro, who introduced the program, did not allocate sufficient funding to continue it in the 2023 budget.
“We can’t start 2023 without the ‘Auxilio’ and a real increase in the minimum wage,” the leader of Lula’s Workers’ Party, Gleisi Hoffmann, said Friday.
“That’s our contract with the Brazilian people.”
Facing the impossible math of funding such pledges without breaking the government spending cap, Lula’s allies are exploring their options, including passing a constitutional amendment allowing exceptional spending next year.
But they are racing the clock: it would have to be approved by December 15.
Markets watching
Lula, who ran on vague promises of restoring Latin America’s biggest economy to the golden times of his first two terms (2003-2010), faces a bleaker picture this time around.
“The challenge is… how to balance fiscal responsibility with a highly anticipated social agenda,” in the face of high inflation and a possible global recession, said political scientist Leandro Consentino of Insper university.
Markets are watching closely — especially his pick for finance minister.
Lula is expected to split Bolsonaro’s economy “super-ministry” into three portfolios: finance, planning, and trade and industry.
Analysts predict a political choice for finance minister, a technocrat for planning and a business executive for trade.
Names floated for the finance job include Lula’s former education minister Fernando Haddad and his campaign coordinator, Aloizio Mercadante.
COP27 stage
Other closely watched portfolios are the environment and a promised new ministry of Indigenous affairs — both sore spots under Bolsonaro, who presided over a surge of destruction in the Amazon rainforest.
The former job could go to Lula’s one-time environment minister Marina Silva, credited with curbing deforestation in the 2000s.
In a key gesture, the president-elect will make his return to the international stage at the COP27 UN climate summit in Egypt, where he will arrive on November 14, advisers said.
Silva, who will travel with him, told newspaper Folha de Sao Paulo: “The climate issue is now a strategic priority at the highest level.”
International
Peruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge

Peru is facing an unprecedented surge in crime ahead of its presidential election scheduled for April 12, with violence fueled by extortion networks and a wave of contract killings linked to organized crime.
Police data show that 2,200 homicides tied to organized crime were recorded in 2025, while extortion complaints increased by 19%, underscoring the growing security crisis in the South American nation.
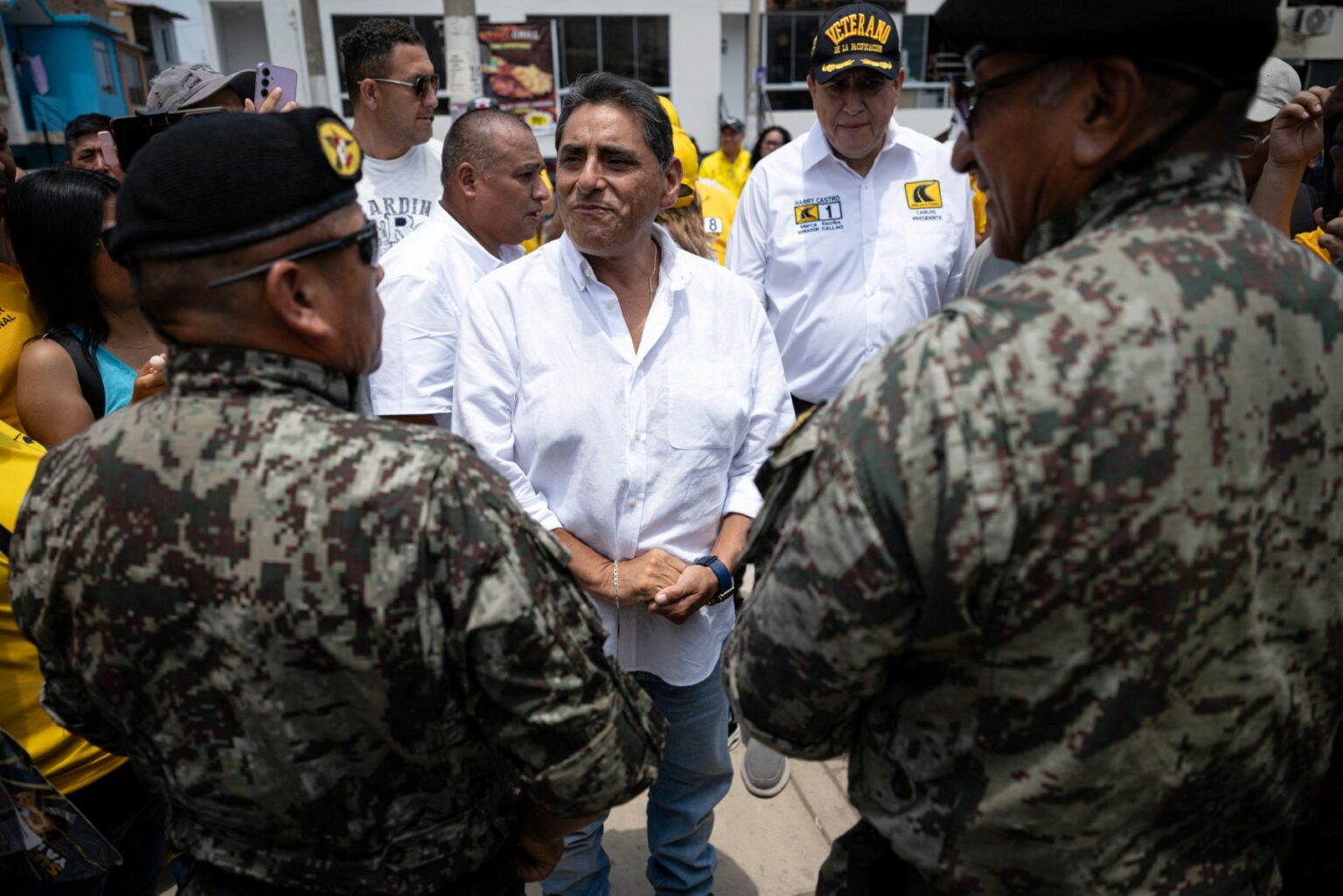
Amid this backdrop, presidential candidate Álvarez has proposed reinstating the death penalty if elected, arguing that extreme measures are needed to curb the violence.
To implement the proposal, Álvarez said Peru would withdraw from the American Convention on Human Rights—also known as the Pact of San José—which the country signed in 1978. The agreement prevents member states that have abolished capital punishment from reinstating it.
Currently, Peruvian law only allows the death penalty in cases of treason during wartime.
“We have to leave the Pact of San José and apply the death penalty in Peru because those miserable criminals don’t deserve to live,” Álvarez told AFP during a campaign stop at a market in Callao, the port city neighboring Lima.
“An iron fist against those criminals,” he added, proposing to declare hitmen as military targets.
During the campaign event, Álvarez walked through stalls selling vegetables, groceries, and fish, greeting vendors while musicians played cumbia music nearby.
The 62-year-old candidate, who spent more than four decades working in television as a comedian, is a newcomer to politics and is running for president under the País para Todos party.
Polls place him fifth in voter preference with nearly 4% support in a fragmented race featuring 36 candidates.
“I am an artist who has taken a step into politics to bring peace to my country,” Álvarez told reporters while surrounded by supporters.
International
FBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot

The man who died during Thursday’s attack on a synagogue in the United States suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head, according to the FBI.
FBI agent Jennifer Runyan told reporters that the suspect, identified as 41-year-old Lebanese citizen Ayman Mohamad Ghazali, shot himself at some point during the confrontation.
“At some point during the shooting, Ghazali suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head,” Runyan said during a press conference.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security confirmed the suspect’s identity.
Authorities said Ghazali drove a truck into the Temple Israel synagogue in West Bloomfield, located in the state of Michigan, on Thursday.
According to Michael Bouchard, sheriff of Oakland County, synagogue security personnel noticed the vehicle and confronted the suspect with gunfire.
Investigators said it would be premature to speculate about the motive for the attack, although reports indicate Ghazali recently lost relatives during Israeli strikes in Lebanon earlier this month.
“It would be irresponsible for me to speculate about his motive,” Runyan said.
Ghazali arrived in Detroit in 2011 on a spouse visa for U.S. citizens and obtained American citizenship in 2016, according to reporting by The New York Times.
He was the father of two teenagers, divorced from his wife in 2024, and had recently been working as a waiter.
The newspaper also reported that Ghazali attended a memorial service in the nearby city of Dearborn for relatives killed in the recent conflict, alongside other grieving family members from the Lebanese town of Machghara.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation said the incident is being investigated as an act of violence targeting the Jewish community.
A source from Michigan’s Lebanese-American community told CBS News that several of Ghazali’s relatives had been killed roughly ten days before the attack, leaving him deeply devastated.
International
Mexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba
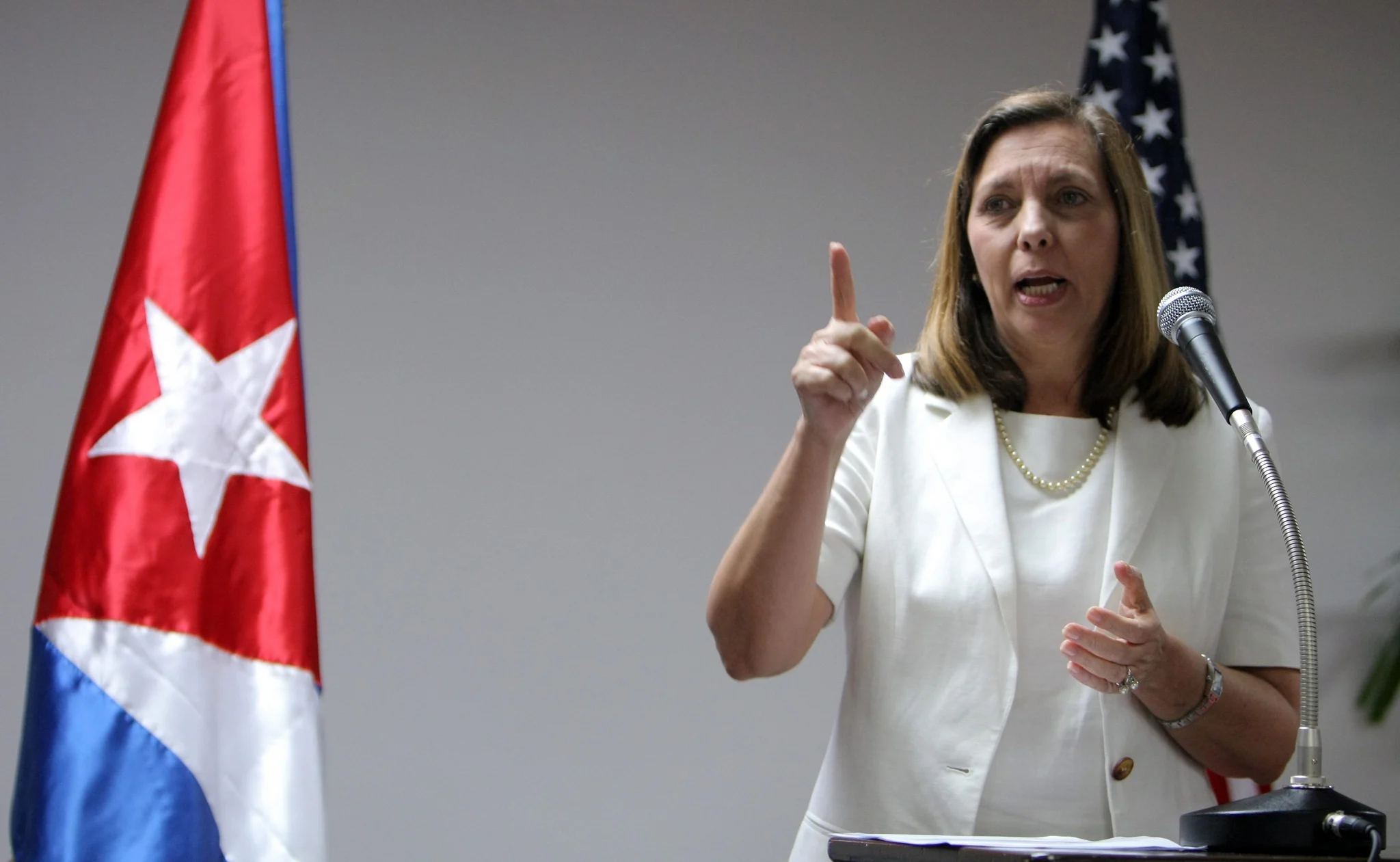

Two logistics support vessels from the Mexican Navy — the ARM Papaloapan and the ARM Huasteco — docked again on Friday in the bay of Havana carrying a third shipment of humanitarian aid for Cuba.
The vessels had previously arrived on the Caribbean island on February 28 with a second cargo that included 1,200 tons of food, sent to help alleviate the country’s ongoing crisis, which has worsened following the U.S. oil restrictions affecting fuel supplies to the island.
Cuba’s deputy foreign minister Josefina Vidal confirmed the new shipment in a social media post.
“Two ships carrying a third shipment of aid from the Government and the people of Mexico for the Cuban people are now arriving at the port of Havana. Thank you Mexico for your solidarity with Cuba,” she wrote.
Previous aid shipments
During the second shipment, the Papaloapan transported 1,078 tons of beans and powdered milk, while the Huastecocarried 92 tons of beans and 23 tons of assorted food products collected by social organizations with support from the government of Mexico City.
In recent months, Mexico has become the largest provider of humanitarian aid to Cuba, sending around 2,000 tons of supplies, mostly staple foods and hygiene products, in the two shipments prior to Friday’s delivery.
The first shipment alone included 814 tons of food.
Cuba praises Mexico’s support
Hours before the ships arrived, Cuban President Miguel Díaz-Canel highlighted Mexico’s support during a televised appearance, describing the country as “a friendly and brotherly nation that has shown tremendous solidarity,”particularly praising Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum.
Díaz-Canel also addressed reports suggesting that Mexican donations were being resold in state-run stores, dismissing them as a “disinformation campaign” promoted by right-wing groups.
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoU.S. Confirms Death of Six Crew Members in KC-135 Crash in Western Iraq
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoGuatemala Remains in “Restricted” Press Freedom Category, Chapultepec Index Warns
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump Says Iran Is Welcome at 2026 World Cup but Warns of Security Concerns
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoIran issues threat to Trump as conflict escalates over Strait of Hormuz
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Report Warns of Nicaragua’s “Transnational” Surveillance Network Targeting Dissidents
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoTrump Raises Possibility of “Friendly Takeover” of Cuba Amid Deepening Crisis
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoFBI Warns of Possible Iranian Drone Attack on U.S. West Coast
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoDriver detained after suspicious vehicle incident near the White House
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoEcuador Declares 60-Day National Emergency After Deadly Floods and Landslides
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoMexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba
-

 Sin categoría3 days ago
Sin categoría3 days agoUN experts warn Nicaragua runs vast transnational network to monitor exiled dissidents
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTrump Pushes for Regime Change in Cuba as Havana Confirms Talks With Washington
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Rapporteur Warns of “Deep Crisis” in Guatemala’s Judicial System
-

 International7 hours ago
International7 hours agoFBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot
-

 International7 hours ago
International7 hours agoPeruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge
-

 Sin categoría2 days ago
Sin categoría2 days agoFBI Most Wanted Fugitive Arrested in Mexico and Deported to U.S.