International
Bacterial infections the ‘second leading cause of death worldwide’
| By AFP |
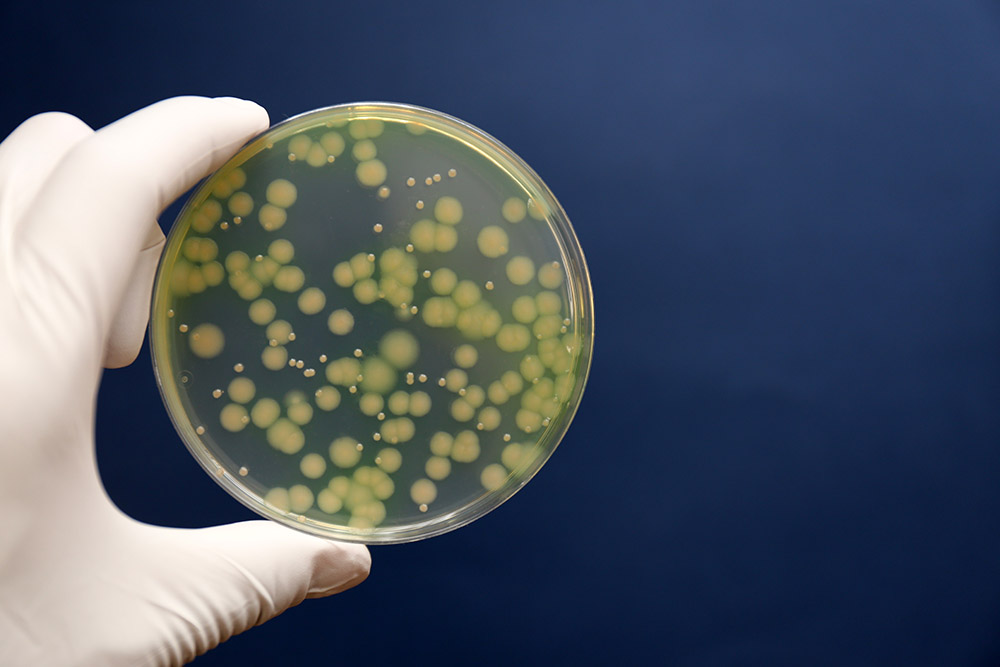
Bacterial infections are the second leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for one in eight of all deaths in 2019, the first global estimate of their lethality revealed on Tuesday.
The massive new study, published in the Lancet journal, looked at deaths from 33 common bacterial pathogens and 11 types of infection across 204 countries and territories.
The pathogens were associated with 7.7 million deaths — 13.6 percent of the global total — in 2019, the year before the Covid-19 pandemic took off.
That made them the second-leading cause of death after ischaemic heart disease, which includes heart attacks, the study said.
Just five of the 33 bacteria were responsible for half of those deaths: Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
S. aureus is a bacterium common in human skin and nostrils but behind a range of illnesses, while E. coli commonly causes food poisoning.
The study was conducted under the framework of the Global Burden of Disease, a vast research programme funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation involving thousands of researchers across the world.
“These new data for the first time reveal the full extent of the global public health challenge posed by bacterial infections,” said study co-author Christopher Murray, the director of US-based Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation.
“It is of utmost importance to put these results on the radar of global health initiatives so that a deeper dive into these deadly pathogens can be conducted and proper investments are made to slash the number of deaths and infections.”
The research points to stark differences between poor and wealthy regions.
In Sub-Saharan Africa, there were 230 deaths per 100 000 population from the bacterial infections.
That number fell to 52 per 100,000 in what the study called the “high-income super-region” which included countries in Western Europe, North America and Australasia.
The authors called for increased funding, including for new vaccines, to lessen the number of deaths, also warning against “unwarranted antibiotic use”.
Hand washing is among the measures advised to prevent infection.
International
Mexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba

Two logistics support vessels from the Mexican Navy — the ARM Papaloapan and the ARM Huasteco — docked again on Friday in the bay of Havana carrying a third shipment of humanitarian aid for Cuba.
The vessels had previously arrived on the Caribbean island on February 28 with a second cargo that included 1,200 tons of food, sent to help alleviate the country’s ongoing crisis, which has worsened following the U.S. oil restrictions affecting fuel supplies to the island.
Cuba’s deputy foreign minister Josefina Vidal confirmed the new shipment in a social media post.
“Two ships carrying a third shipment of aid from the Government and the people of Mexico for the Cuban people are now arriving at the port of Havana. Thank you Mexico for your solidarity with Cuba,” she wrote.
Previous aid shipments
During the second shipment, the Papaloapan transported 1,078 tons of beans and powdered milk, while the Huastecocarried 92 tons of beans and 23 tons of assorted food products collected by social organizations with support from the government of Mexico City.
In recent months, Mexico has become the largest provider of humanitarian aid to Cuba, sending around 2,000 tons of supplies, mostly staple foods and hygiene products, in the two shipments prior to Friday’s delivery.
The first shipment alone included 814 tons of food.
Cuba praises Mexico’s support
Hours before the ships arrived, Cuban President Miguel Díaz-Canel highlighted Mexico’s support during a televised appearance, describing the country as “a friendly and brotherly nation that has shown tremendous solidarity,”particularly praising Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum.
Díaz-Canel also addressed reports suggesting that Mexican donations were being resold in state-run stores, dismissing them as a “disinformation campaign” promoted by right-wing groups.
International
Ecuador Declares 60-Day National Emergency After Deadly Floods and Landslides

Ecuador has declared a 60-day national emergency to address the impact of a severe rainy season that has left 11 people dead and more than 50,000 affected since January, the government’s disaster management authority announced Friday.
Prolonged heavy rains accompanied by thunderstorms have caused river overflows and landslides, mainly in the coastal provinces of Guayas, El Oro, Esmeraldas, Los Ríos, Manabí and Santa Elena, as well as in the Andean provinces of Lojaand Chimborazo.
According to the Secretariat for Risk Management of Ecuador, the emergency declaration was issued “due to the level of impact caused nationwide on the population, the road network, infrastructure, and livelihoods.”
“The emergency declaration is aimed at responding to the effects and negative impacts and preventing their further spread,” the agency said in a statement.
International
Trump Pushes for Regime Change in Cuba as Havana Confirms Talks With Washington

U.S. President Donald Trump has made no secret of his desire for political change in Cuba, located just 150 kilometers from the United States. Washington considers the island an “exceptional threat,” citing its close ties with Russia, Chinaand Iran, longtime allies of Havana.
Trump has urged Cuba to “reach a deal” with Washington or face consequences, as the island struggles with a severe energy crisis that has nearly paralyzed its economy after the United States cut oil shipments from Venezuela, its main fuel supplier. The U.S. has also warned other countries against selling fuel to Havana.
Cuban President Miguel Díaz-Canel confirmed that Cuban officials have recently held talks with representatives of the U.S. government. The statement came during a meeting with senior members of the ruling Communist Party of Cuba and the executive committee of the Council of Ministers, according to footage broadcast on Cuban television.
“These conversations have been aimed at seeking solutions through dialogue to the bilateral differences that exist between our two nations,” Díaz-Canel said.
Reports of intermediaries and possible negotiations
According to television images, among those attending the meeting was Raúl Guillermo Rodríguez Castro, grandson of former Cuban leader Raúl Castro. Although he holds no official government position, U.S. media have identified him as a possible interlocutor with U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio in what have been described as secret discussions between Washington and Havana.
For some Cubans, any potential agreement with Washington is viewed pragmatically. “As long as it benefits us, we can reach an agreement — but on our terms,” said Sergio Guerra, a 55-year-old agricultural vendor, speaking to AFP.
Díaz-Canel’s remarks confirm earlier statements by Trump, who indicated in January that his administration had already begun contacts with senior Cuban officials.
Mexico calls for diplomacy
Meanwhile, Mexico welcomed the possibility of dialogue after recently sending more than 2,000 tons of humanitarian aid to Cuba to help mitigate the crisis.
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum said her country would always promote peace and diplomatic dialogue, particularly in response to what she described as the long-standing injustice of the U.S. embargo on the Cuban people.
-

 Central America3 days ago
Central America3 days agoGuatemala Remains in “Restricted” Press Freedom Category, Chapultepec Index Warns
-

 International14 hours ago
International14 hours agoU.S. Confirms Death of Six Crew Members in KC-135 Crash in Western Iraq
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoTrump Says Iran Is Welcome at 2026 World Cup but Warns of Security Concerns
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoIran issues threat to Trump as conflict escalates over Strait of Hormuz
-

 Central America3 days ago
Central America3 days agoUN Report Warns of Nicaragua’s “Transnational” Surveillance Network Targeting Dissidents
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoTrump Raises Possibility of “Friendly Takeover” of Cuba Amid Deepening Crisis
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoFBI Warns of Possible Iranian Drone Attack on U.S. West Coast
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoDriver detained after suspicious vehicle incident near the White House
-

 Sin categoría2 days ago
Sin categoría2 days agoUN experts warn Nicaragua runs vast transnational network to monitor exiled dissidents
-

 International14 hours ago
International14 hours agoEcuador Declares 60-Day National Emergency After Deadly Floods and Landslides
-

 International13 hours ago
International13 hours agoMexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba
-

 Central America3 days ago
Central America3 days agoUN Rapporteur Warns of “Deep Crisis” in Guatemala’s Judicial System
-

 International14 hours ago
International14 hours agoTrump Pushes for Regime Change in Cuba as Havana Confirms Talks With Washington
-

 Sin categoría1 day ago
Sin categoría1 day agoFBI Most Wanted Fugitive Arrested in Mexico and Deported to U.S.


































