International
Latin American leaders hold summit with Brazil back in the fold

January 24 | By AFP | Philippe Bernes-Lasserre / Mauricio Rabuffetti |
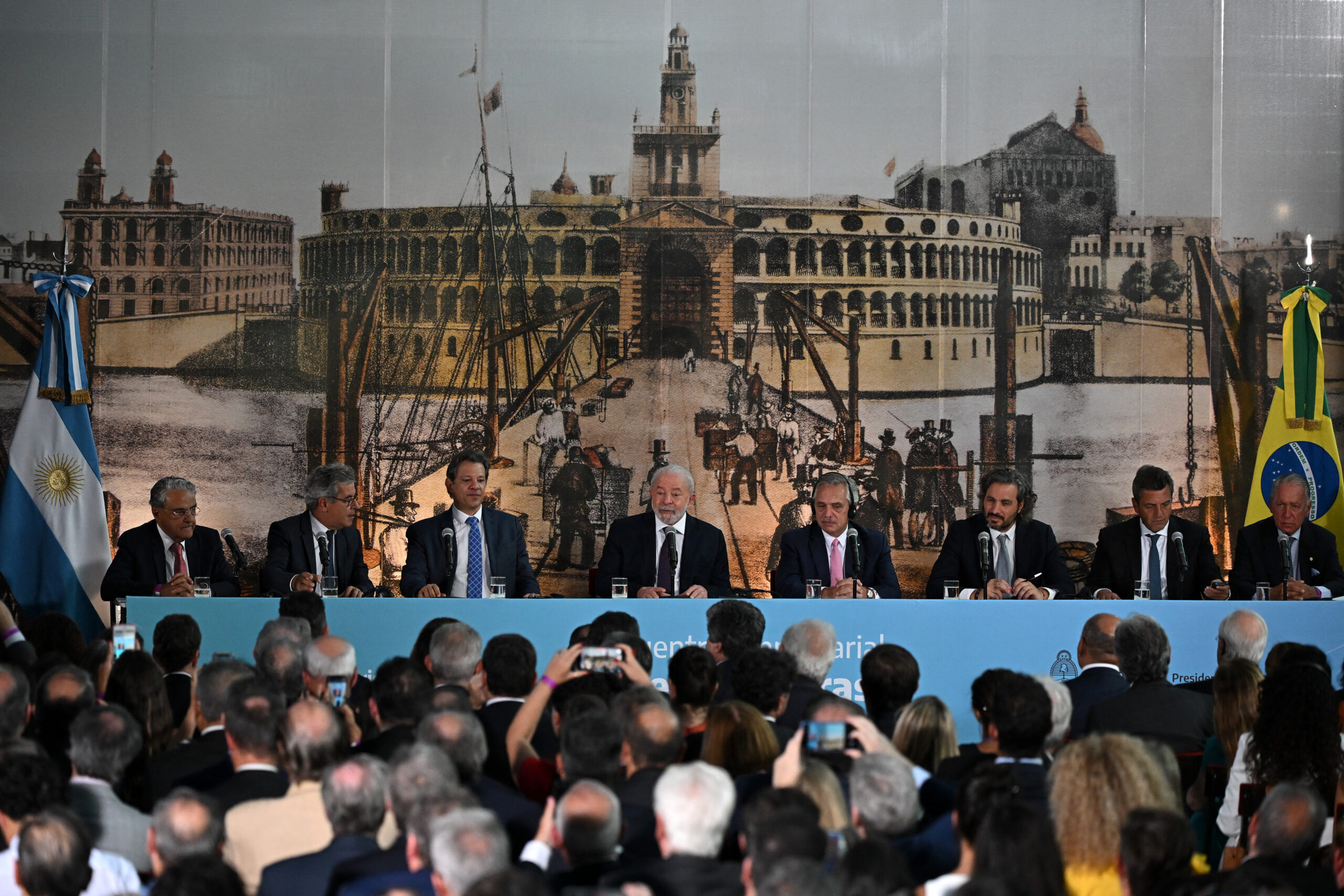
Fifteen Latin American heads of state and government meet Tuesday in Buenos Aires for a regional summit welcoming back Brazil as President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva looks to rebuild bridges after his far-right predecessor Jair Bolsonaro pulled out of the grouping.
The 77-year-old Lula, in Argentina for the first international trip of his third term, will participate in the seventh Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC) summit, bringing together 33 states from the region.
Lula was one of the founders of CELAC, during the first “pink wave” on the continent in the first decade of the century.
And now he brings Brazil back into the fold after Bolsonaro had suspended the country’s participation in the grouping.
Host Argentina this week hailed a “new climate in Latin America”, with the region ushering in a new wave of left or center-left governments since 2018, including Mexico, Argentina, Honduras, Chile, Colombia and Brazil.
A forum for consultation and cooperation, CELAC is not a regional integration mechanism with binding opinions.
And for all the importance underlined on Monday by Argentine President Alberto Fernandez and Lula of “the need to integrate Latin America,” CELAC is struggling to unite members over successive regional crises, like Peru.
“Latin America is bankrupt from the institutional point of view (…) it has not succeeded in integrating collectively into the world,” Ignacio Bartesaghi, an expert in international relations at the Catholic University of Uruguay, told AFP.
At the very least, CELAC “remains a vast and diverse space of Latin American countries from which minimal agendas or common interests for the region can be established”, agreed Bernabe Malacalza, researcher in international relations at the Argentine national research center CONICET.
“There is not even certain basic consensus in Latin America, as on the difference between a democracy and a dictatorship,” Bartesaghi stressed.
“There are (at CELAC) presidents who do not even recognize each other,” he noted.
Like Paraguay’s Mario Abdo Benitez, whose country broke diplomatic relations with Nicolas Maduro’s Venezuela in 2019.
Lula meanwhile has pledged to reopen the embassies.
‘Rebuild Mercosur!’
Maduro at last minute called off his trip, citing “a risk of aggression” from “the neo-fascist right,” a possible reference to some Argentine opposition politicians calling for him to be arrested on arrival.
Other significant absentees in Buenos Aires include Mexico’s leftwing President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador, leader of the second largest economy in Latin America and host in 2021 of the last CELAC summit.
CELAC however remains the interlocutor of choice for China, or the EU to negotiate cooperation agendas with the region.
But even here, “The impossibility of holding an EU-CELAC summit since the last one in 2015 (in Brussels) illustrates (…), the absence of a solid biregional political dialogue,” Malacalza said.
In this sense, the return of Lula could give a boost to certain sub-regional issues, such as the free-trade agreement between the EU and the Mercosur group which comprises Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay.
The deal was finalized in 2019 but never ratified, due in particular to concerns about Bolsonaro’s environmental policy.
Lula has indicated a willingness to resume contacts.
“We are going to rebuild Mercosur!” Lula said Monday evening, referring to the customs union which has been torn in recent months over a free trade treaty with China.
“We will recreate Unasur!” he continued, referring to the moribund Union of South American Nations created in 2008 on the initiative of himself and Venezuela’s Hugo Chavez.
Latin America is only the initial phase of the Brazilian president’s international push, with Lula heading to Washington in February and to China “after March.”
International
Peruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge

Peru is facing an unprecedented surge in crime ahead of its presidential election scheduled for April 12, with violence fueled by extortion networks and a wave of contract killings linked to organized crime.
Police data show that 2,200 homicides tied to organized crime were recorded in 2025, while extortion complaints increased by 19%, underscoring the growing security crisis in the South American nation.
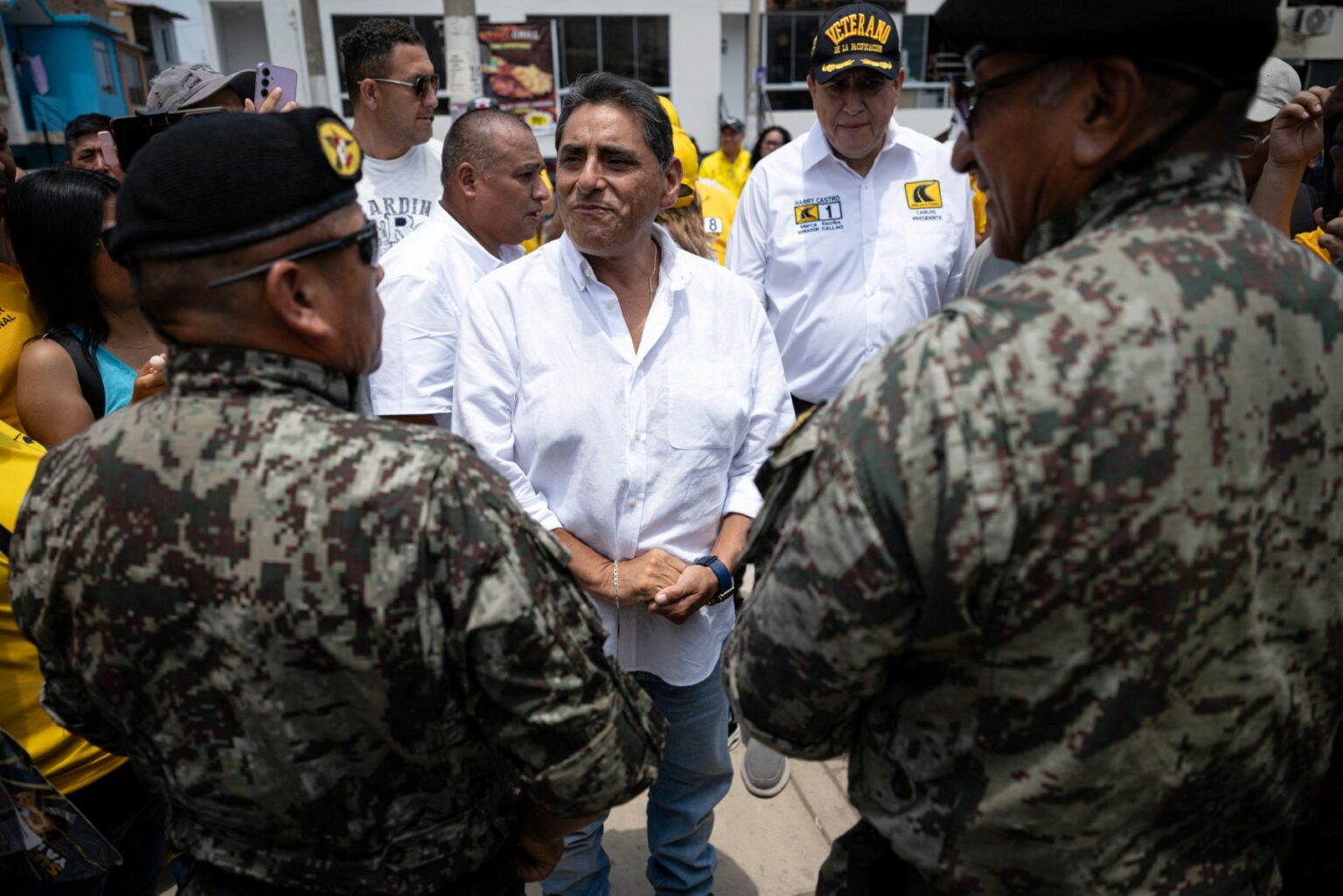
Amid this backdrop, presidential candidate Álvarez has proposed reinstating the death penalty if elected, arguing that extreme measures are needed to curb the violence.
To implement the proposal, Álvarez said Peru would withdraw from the American Convention on Human Rights—also known as the Pact of San José—which the country signed in 1978. The agreement prevents member states that have abolished capital punishment from reinstating it.
Currently, Peruvian law only allows the death penalty in cases of treason during wartime.
“We have to leave the Pact of San José and apply the death penalty in Peru because those miserable criminals don’t deserve to live,” Álvarez told AFP during a campaign stop at a market in Callao, the port city neighboring Lima.
“An iron fist against those criminals,” he added, proposing to declare hitmen as military targets.
During the campaign event, Álvarez walked through stalls selling vegetables, groceries, and fish, greeting vendors while musicians played cumbia music nearby.
The 62-year-old candidate, who spent more than four decades working in television as a comedian, is a newcomer to politics and is running for president under the País para Todos party.
Polls place him fifth in voter preference with nearly 4% support in a fragmented race featuring 36 candidates.
“I am an artist who has taken a step into politics to bring peace to my country,” Álvarez told reporters while surrounded by supporters.
International
FBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot

The man who died during Thursday’s attack on a synagogue in the United States suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head, according to the FBI.
FBI agent Jennifer Runyan told reporters that the suspect, identified as 41-year-old Lebanese citizen Ayman Mohamad Ghazali, shot himself at some point during the confrontation.
“At some point during the shooting, Ghazali suffered a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head,” Runyan said during a press conference.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security confirmed the suspect’s identity.
Authorities said Ghazali drove a truck into the Temple Israel synagogue in West Bloomfield, located in the state of Michigan, on Thursday.
According to Michael Bouchard, sheriff of Oakland County, synagogue security personnel noticed the vehicle and confronted the suspect with gunfire.
Investigators said it would be premature to speculate about the motive for the attack, although reports indicate Ghazali recently lost relatives during Israeli strikes in Lebanon earlier this month.
“It would be irresponsible for me to speculate about his motive,” Runyan said.
Ghazali arrived in Detroit in 2011 on a spouse visa for U.S. citizens and obtained American citizenship in 2016, according to reporting by The New York Times.
He was the father of two teenagers, divorced from his wife in 2024, and had recently been working as a waiter.
The newspaper also reported that Ghazali attended a memorial service in the nearby city of Dearborn for relatives killed in the recent conflict, alongside other grieving family members from the Lebanese town of Machghara.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation said the incident is being investigated as an act of violence targeting the Jewish community.
A source from Michigan’s Lebanese-American community told CBS News that several of Ghazali’s relatives had been killed roughly ten days before the attack, leaving him deeply devastated.
International
Mexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba

Two logistics support vessels from the Mexican Navy — the ARM Papaloapan and the ARM Huasteco — docked again on Friday in the bay of Havana carrying a third shipment of humanitarian aid for Cuba.
The vessels had previously arrived on the Caribbean island on February 28 with a second cargo that included 1,200 tons of food, sent to help alleviate the country’s ongoing crisis, which has worsened following the U.S. oil restrictions affecting fuel supplies to the island.
Cuba’s deputy foreign minister Josefina Vidal confirmed the new shipment in a social media post.
“Two ships carrying a third shipment of aid from the Government and the people of Mexico for the Cuban people are now arriving at the port of Havana. Thank you Mexico for your solidarity with Cuba,” she wrote.
Previous aid shipments
During the second shipment, the Papaloapan transported 1,078 tons of beans and powdered milk, while the Huastecocarried 92 tons of beans and 23 tons of assorted food products collected by social organizations with support from the government of Mexico City.
In recent months, Mexico has become the largest provider of humanitarian aid to Cuba, sending around 2,000 tons of supplies, mostly staple foods and hygiene products, in the two shipments prior to Friday’s delivery.
The first shipment alone included 814 tons of food.
Cuba praises Mexico’s support
Hours before the ships arrived, Cuban President Miguel Díaz-Canel highlighted Mexico’s support during a televised appearance, describing the country as “a friendly and brotherly nation that has shown tremendous solidarity,”particularly praising Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum.
Díaz-Canel also addressed reports suggesting that Mexican donations were being resold in state-run stores, dismissing them as a “disinformation campaign” promoted by right-wing groups.
-

 International22 hours ago
International22 hours agoU.S. Confirms Death of Six Crew Members in KC-135 Crash in Western Iraq
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoGuatemala Remains in “Restricted” Press Freedom Category, Chapultepec Index Warns
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoTrump Says Iran Is Welcome at 2026 World Cup but Warns of Security Concerns
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoIran issues threat to Trump as conflict escalates over Strait of Hormuz
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Report Warns of Nicaragua’s “Transnational” Surveillance Network Targeting Dissidents
-

 International4 days ago
International4 days agoTrump Raises Possibility of “Friendly Takeover” of Cuba Amid Deepening Crisis
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoFBI Warns of Possible Iranian Drone Attack on U.S. West Coast
-

 International3 days ago
International3 days agoDriver detained after suspicious vehicle incident near the White House
-

 International22 hours ago
International22 hours agoEcuador Declares 60-Day National Emergency After Deadly Floods and Landslides
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours agoMexican Navy Ships Deliver Third Shipment of Humanitarian Aid to Cuba
-

 Sin categoría3 days ago
Sin categoría3 days agoUN experts warn Nicaragua runs vast transnational network to monitor exiled dissidents
-

 Central America4 days ago
Central America4 days agoUN Rapporteur Warns of “Deep Crisis” in Guatemala’s Judicial System
-

 International22 hours ago
International22 hours agoTrump Pushes for Regime Change in Cuba as Havana Confirms Talks With Washington
-

 Sin categoría2 days ago
Sin categoría2 days agoFBI Most Wanted Fugitive Arrested in Mexico and Deported to U.S.
-

 International37 minutes ago
International37 minutes agoFBI: Man who attacked Michigan synagogue died from self-inflicted gunshot
-

 International35 minutes ago
International35 minutes agoPeruvian presidential candidate proposes death penalty amid crime surge